SVG control package v2.3
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an XML-based vector image format for two dimensional graphics developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
The "SVG control package" enables the use of Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) in Delphi and FPC Lazarus applications. The current version of the package covers most of the SVG 1.1 specification, with the exception of SMIL animation and scripting.
The architecture of the software allows for use on multiple platforms. The software can be used in Delphi VCL, FMX and Lazarus applications for Windows, OsX and Linux targets. Mobile platforms iOS and Android are to some extend possible but with limitations. Other targets might also be possible but these are not tried or tested.
The requirements for the package are the following:
- For Delphi: Delphi XE2 or later.
- For FPC Lazarus version 3.0.4 and Lazarus 1.8.4 or including the rtl-generics package.
You can just use the controls provided in the package or you can go a bit deeper and try the programming examples. The programming examples show how to interact with the SVG content, or how to animate the graphic, not with SMIL but with Pascal code.
In this help file you will find the following:
- How to install the package in Delphi and Lazarus
- Information about the use and architecture of the software
- Information about coverage of the SVG 1.1 specification
- Programming examples
- Contact, bug reporting and licensing info
Please read the installation instructions carefully!
Delphi installation
Installation packages in Delphi
Remove old versions
If older versions of the SVG control version packages are already installed, these have to be removed first.
Choose "Install Packages..." in the IDE.

Then deselect and remove the packages named
DclSVG2PackageFmx.bpl,
DclSVG2PackageVcl.bpl and
DclSVG2PackageCommon.bpl. Remove the Fmx and Vcl package first because these are dependent on the Common package.

It might be necessary to check if really all old files are deleted and no old package files or object files remain on the file path. Otherwise you might experience strange behaviour in Delphi, for example exception errors on closing Delphi.
Next, before you reinstall the new packages RESTART DELPHI!
Install the new versions.
For each Delphi version there are in total 6 packages, 3 run-time packages and 3 design-time packages.
Depending on your Delphi version, you can find find the package files in the sub folder indicated by the following table.
| Folder | Delphi name | ID | Compiler version |
|---|---|---|---|
| XE2 | Delphi XE2 | XE2 | 23 |
| XE3 | Delphi XE3 | XE3 | 24 |
| XE4 | Delphi XE4 | XE4 | 25 |
| XE5 | Delphi XE5 | XE5 | 26 |
| XE6 | Delphi XE6 | XE6 | 27 |
| XE7 | Delphi XE7 | XE7 | 28 |
| XE8 | Delphi XE8 | XE8 | 29 |
| DX | Delphi 10 Seattle | DX | 30 |
| DX1 | Delphi 10.1 Berlin | DX1 | 31 |
| DX2 | Delphi 10.2 Tokyo | DX2 | 32 |
| DX3 | Delphi 10.3 Rio | DX3 | 33 |
So, the package that ends with
..XE5.dproj should be installed in Delphi XE5 and
..DX1.dproj should be installed in Delphi DX1 Berlin.
The run-time packages contain the actual SVG source code units, there is a common package, a package for Vcl and one for FMX. The run-time packages must at least be build to target Win32 and if you want to use the SVG package in 64 bit applications, you have to build the run time packages to target Win64 also.
-
SVG2PackageCommon<ID> -
SVG2PackageFmx<ID> -
SVG2PackageVcl<ID>
The design-time packages start with "Dcl..." and contain the units to register the package in the Delphi IDE and the property editors. These packages can only be build to target Win32, because the Delphi IDE is a 32bit application.
-
DclSVG2PackageCommon<ID> -
DclSVG2PackageFmx<ID> -
DclSVG2PackageVcl<ID>
Here is an example how to build the packages and in case of the design-time packages how to install them. In this example I use Delphi DX1 Berlin and only build the packages to the default Win32 target.
The run-time common package
SVG2PackageCommonDX1 has to be build first because the other packages are dependent.
1. In the IDE choose "File - Open Project..." and open the project file
SVG2PackageCommonDX1.dproj in de
Package folder of relevant Delphi version.

2. Build
SVG2PackageCommonDX1, you can save the changes if asked for
3. Open project file
DclSVG2PackageCommonDX1.dproj.
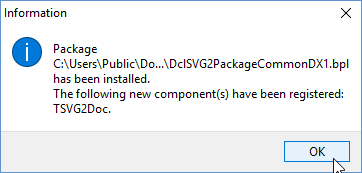
4. Build and then Install package
DclSVG2PackageCommon.DX1.
After installation there will be a notification that one component has been registered: TSVG2Doc.
5. Next open the project file
SVG2PackageFmxDX1.dproj in the sub folder
Fmx of the package folder.

6. Build package
SVG2PackageFmxDX1.
7. Open the project file
DclSVG2PackageFmxDX1.dproj.
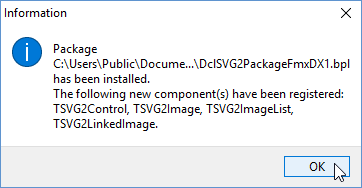
8. Build an then Install package
DclSVG2PackageFmxDX1.
After installation there will be a notification that four new components have been registered: TSVG2Control, TSVG2Image, TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImage.
9. Next open the project file
SVG2PackageVclDX1.dproj in the sub folder
Vcl of the package folder.

10. Build package
SVG2PackageVclDX1.
11. Open the project file
DclSVG2PackageVclDX1.dproj.
12. Build and then Install package
DclSVG2PackageVclDX1.
After installation there will be a notification that four new components have been registered: TSVG2Control, TSVG2Image, TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImage.

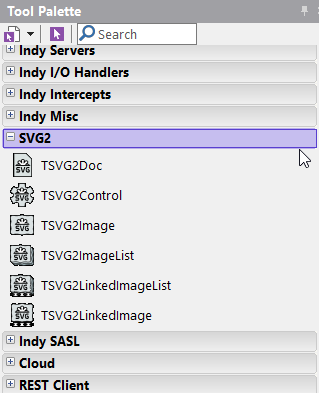
After installing these packages, there should be a group called SVG2 in the Tool palette containing 5 components in FMX and 6 components in VCL: TSVG2Doc, TSVG2Control, TSVG2Image, TSVG2ImageList, TSVG2LinkedImageList (VCL only), TSVG2LinkedImage.
Setting up the Delphi project environment
To be able to compile your Delphi projects with the SVG package, Delphi needs to know where the source code of the package is located. There are three ways to set this up:
- Add folders to your library path once.
- Add a search path to your new projects in the project options
- Add the SVG package units to your new projects explicitly
Add folders to your library path once
This might be the most convenient because you have to do it only once.
- Select "Tools -> Options" from the Delphi menu.
- Select the "Library" page.
- Select a platform, 32-bit Windows, 64-bit Windows, OSX etc. You must add the paths for each platform.
- Add the path to the
Commonfolder of the SVG package to the library path. - Next, for VCL applications, add the path to
Common\Vcl. - For FMX applications, add the path to
Common\Fmx. - Last, for Vcl and Fmx, add the path to
Common\Platform.

Add a search path to your new projects in the project options
This you have to do for each new project.
- Open the project options in Delphi.
- Select the "Delphi Compiler" page.
- Expand the "Search path" option.
- Add the path to the
Commonfolder of the SVG package to the "Value from "All configurations - All platforms"" option. - Next, if you are creating a VCL application, add the path to
Common\Vcl. - Or if you are creating a Firemonkey application, add the path to
Common\Fmx. - Last, for Vcl and Fmx, add the path to
Common\Platform.
Add the SVG package units to your new projects explicitly
This you might want to do if you want full control over which units you want to compile into your project, you have to do this also for each new project.
First add all the
.pas files from the SVG package in folder
Common.
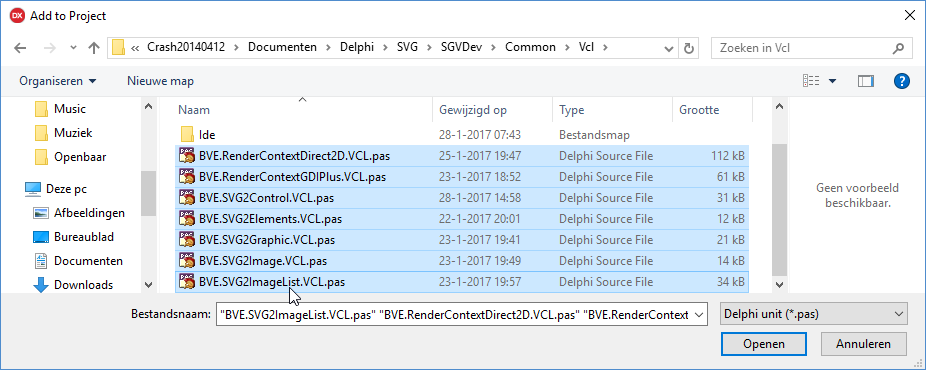
Choose from the Delphi menu "Project ->Add to project". Navigate to the
Common folder of the SVG package and select the files.

VCL application
In case you are creating a VCL application, choose "Project ->Add to project" again and go to the folder
Common\Vcl and select all the files from there.
Next go to folder
Common\Platform. The files you select here depend on the render context you want to use in your application.
The default render context for VCL is Direct2D with a fall back to GDI+.
For this, you have to select all the Direct2D header files (starting with
BVE.DX...), next add
BVE.SVG2ContextD2D.pas and add
BVE.SVG2ContextGP.pas
For rendering text using system fonts, you need to include thetext layoutsalso, so add
BVE.SVG2FontDirectWrite.pas and add
BVE.SVG2FontGDI.pas.
The render context to use for VCL are defined asglobal definesin the include file
Common\Vcl\ContextSettingsVCL.inc. If you want to use another render context than the default, you have to modify this file and include the appropriate files from
Common\Platform into your project.
FMX application
In case you are creating a Firemonkey (FMX) application, choose "Project ->Add to project" again and go to the folder
Common\Fmx and select all the files from there.
Next go to folder
Common\Platform. Again the files you select here depend on the render context you want to use in your application.
The default render context for FMX is "FMX canvas".
For this, you have to select
BVE.SVG2ContextFMX.pas.
The render context to use for FMX are defined in the include file
Common\Fmx\ContextSettingsFMX.inc. If you want to use another render context than the default, you have to modify this file and include the appropriate files from
Common\Platform into your project. See paragraph "Global defines" for details.
A more flexible approach would be to add all the units to your project as described above,exceptthe ones from
Common\Platform. And add a search path to this folder in the project options or in the library path. This way you simply set the render context you want to use in
ContextSettingsVCL.inc or
ContextSettingsFMX.inc and let the system decide which units need to be included.
Test compilation Delphi
Next you can test if your project compiles.
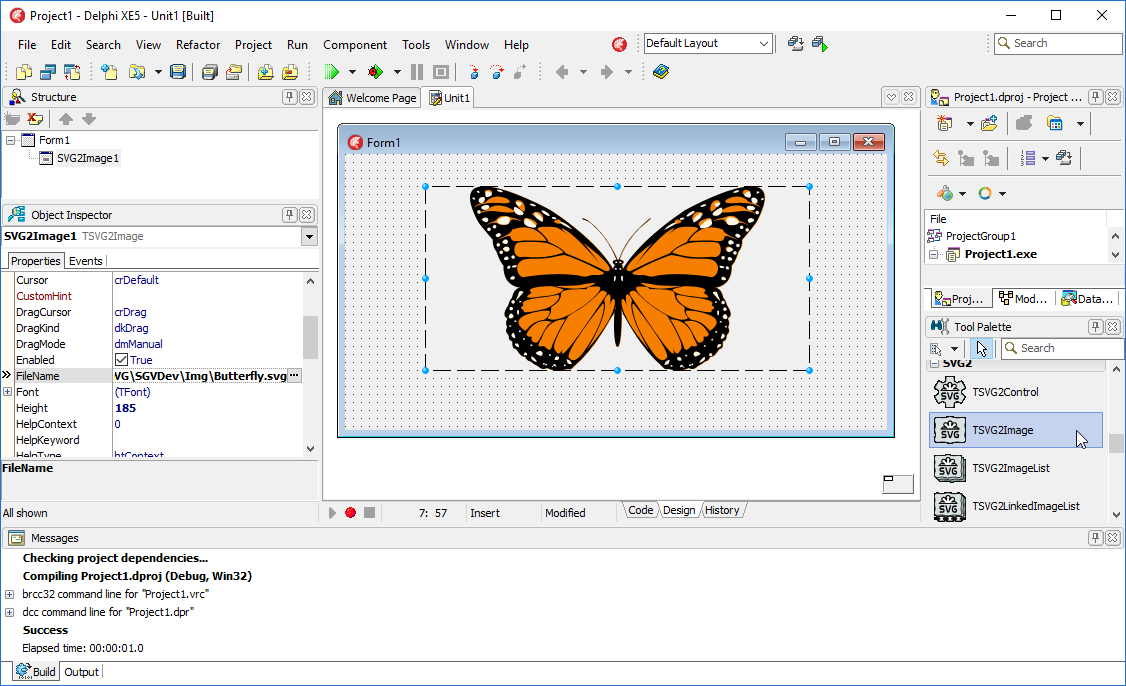
- Create a new project.
- Select the TSVG2Image from the tool palette and put in on the form.
- Select the SVG2Image1 and put a path to an SVG file into the "FileName" property.
- Run the application.
FPC Lazarus installation
FPC and Lazarus requirements for the SVG library
The SVG library is developed with FPC version 3.0.4 and Lazarus version 1.8.4, so it is recommended to use these versions or later.
Also because the SVG library uses generics for lists, stacks and so on, the "rtl-generics" package is needed. This package is provided as standard in FPC 3.1.1.+ but must be downloaded separately for version 3.0.4.
Installation packages in FPC Lazarus
Load the package
FPC\Package\svg2package.lpk into Lazarus IDE:
The package has the following search paths defined:
Common, shared units for all platforms
Common\Fpc, the FPC Lazarus specific units
Common\Platform, the render context interface implementations
Common\Fpc\generics, the "rtl-generics" package. Only include this path if your FPC Lazarus version doesn't include the package by default!
To include the SVG components into the Lazarus IDE, follow these steps:
- Compile the package
- Select Use->Install
Lazarus has to be rebuild to complete the installation.
After installation you will find the SVG controls on tab "SVG2"

Test compilation FPC Lazarus
Test the installation:
- Create a new application project.
- Select the TSVG2Image from the tool palette and put in on the form.
- Select the SVG2Image1 and put a path to an SVG file into the "FileName" property.
- Run the application

SVG components and controls
The SVG package contains the following components and controls.
Components
- TSVG2Doc
- TSVG2ImageList
- TSVG2LinkedImageList
- TSVGGraphic (not available in FMX)
TSVG2Doc

| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2Doc.pas | BVE.SVG2Doc | Xml.XMLDoc.TXMLDocument |
| Fpc | Not available | ||
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2Doc.pas | BVE.SVG2Doc | Xml.XMLDoc.TXMLDocument |
Description
The TSVGDoc is basically a TXMLDocument. It allows for loading SVG content in an XML document without causing error messages.
This might be useful if you want to work with SVG in a IXMLDocument and be able to render it to a bitmap.
The TSVG2Control has a property "SVGDoc" to which you can connect a TSVG2Doc. TSVGDoc is more or less deprecated now, because it is more efficient to parse the SVG from file or from strings than using a TSVGDoc.
TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImageList

TSVG2ImageList is derived from TImageList and therefore contains a list of bitmap images. However, it also contains a list of SVG's and has the capability to automatically create the bitmap images out of the SVG.
The rendering of the bitmap images out of the SVG content occurs when the SVG data is modified or if the TSVGImageList properties are changed, otherwise it just behaves as a static TImageList.
Controls that have a "ImageList" property can also link to a TSVG2ImageList, the control will display the static image from the TSVG2ImageList. If SVG data or some other property of TSVG2ImageList is modified, than the associated static image will be updated and all linked controls will update there image as well.
The image bitmap data along with all the SVG content and settings are stored in the Delphi or FPC/Lazarus form file.
The software for parsing and rendering SVG is complex and adds to the complexity and size of the application you are developing, so it only makes sense to use TSVG2ImageList if you actually need to parse and render images in run-time. An alternative use case could be, to just use a normal TImageList in your main application and develop a small utility application with TSVG2ImageList, from which you export the images that you need in your main application.
Differences between the VCL, FMX and FPC image list
The standard TImageList for VCL, FMX an FPC each differ in design. The main differences are in how scaling is implemented:
-
The VCL image list has been around the longest and is based on the Windows image list which is basically a giant bitmap divided into smaller images each of the same width and height. From Delphi version 10.3 multiple resolutions for scaling are implemented through the "virtual image list" and the "image collection" components. The "virtual image list" samples the bitmap with the resolution it is closest too from the "image collection" component.
The VCL image list also still supports different pixel formats and transparency by masking. But modern 32bit images with alpha channel are of course also possible.
-
The FPC image list for Lazarus until version 1.9 was more or less the same as the VCL image list. From version 1.9 upwards it supports multiple resolutions for scaling. Every resolution is itself an image list, so the FPC TImageList has basically become a list of image lists.
-
The FMX image list was introduced in Delphi XE8. It has a source list of multi resolution bitmaps and it has a destination list that define the actual images. The destination images sample a rectangle from the source bitmaps.
These differences are also present in TSVG2ImageList, because it is derived from TImageList for VCL, FMX and FPC/Lazarus:
-
The TSVG2Imagelist for VCL supports two types of scaling:
-
It can scale the images simply by setting a new "Width" and "Height" and re-render all images.
-
Or the different resolutions can be created beforehand. When scaling occurs the image is sampled from the resolution it is closest too. This resembles how the "virtual image list" and the "image collection" components work. In this the TSVG2imageList is the "image collection" and the TSVG2LinkedImageList is the "virtual image list".
The TSVG2Imagelist for VCL also supports masking and pixel formats other than 32bit. However, al SVG rendering in the package is done on 32bit bitmaps, so if you use other pixel formats, the system has to do an extra conversion.
-
-
The TSVG2Imagelist for FPC version 1.9 and higher supports multiple resolutions for scaling. These must be defined beforehand.
Only 32bit images are supported and no masking.
-
The TSVG2Imagelist for FMX will create one source item with a multi resolution bitmap on which it will draw all images. The resolutions for the multi resolution bitmap must be defined beforehand. The destination list sample rectangles from the source multi resolution bitmap.
Only 32bit images are supported and no masking.
SVG Image lists functionality and settings
The TSVG2ImageList for VCL/FPC Lazarus has the following main functionalities on top of those supplied by the normal TImageList:
- Synthesizing images from SVG definitions
- Creating variations on images using "Styles"
- Creating multiple sizes of images using "Resolutions"
- Exporting images to stream or file
In stead of a list, the TSVG2ImageList can be seen as an image grid, where the rows represent SVG's and the columns represent "Styles" and the "Resolutions" represent different layers of the grid.
The total number of mages you can create with a TSVGImagelist:
SVG count * Style count * Resolution count
The TSVG2LinkedImageList can be used as an intermediate between the controls on the form and a centralized TSVG2ImageList.
The TSVG2LinkedImageList uses all SVG's and all, or one of the "Styles" from a linked parent "TSVG2ImageList" but for the rest has the same properties as a TSVG2ImageList.
Both TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImageList are derived from TSVG2BaseImageList.
- Component editor
- TSVG2LinkedImageList component editor
- Example creating styles
- Example scaling
- Example transparency on VCL and work-around in case of non-themed user interface
Component editor
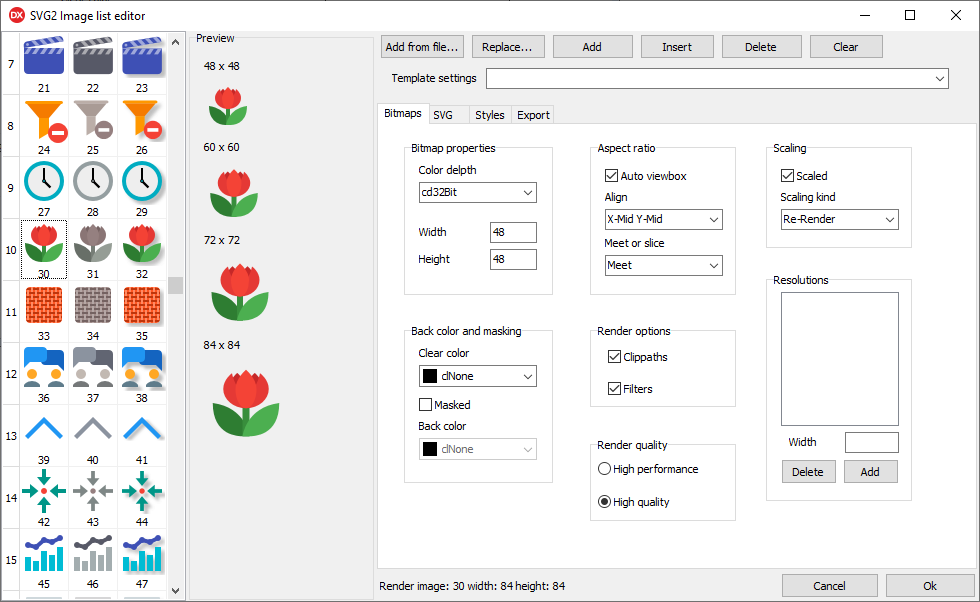
The component editor is activated by double clicking on the TSVG2ImageList component on the form you are designing, or by the pop-up menu that is shown when you right click TSVG2ImageList and then select "Edit...".
VCL TSVG2ImageList component editor
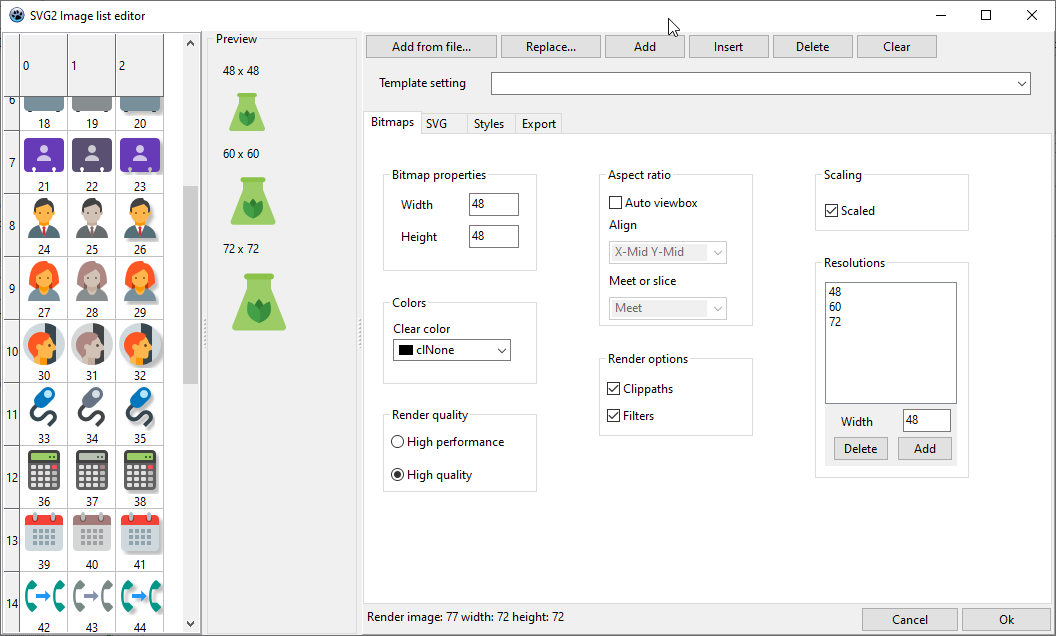
FPC/Lazarus TSVG2ImageList component editor
FMX TSVG2ImageList component editor

-
Image grid
To the left of the component editor there is a grid showing the static images that are contained in the image list. The rows represent the SVG data, the columns represent the styles. A style is applied to all SVG's in the list. The number under the image is the actual image index that you set in a linked control.
Note that inserting an SVG (row) or adding a style (column) will alter the numbering of the images.
-
Preview panel
To the right of the grid, a preview is displayed of the currently selected image in different resolutions.
-
Top row buttons
On the top row are a number of buttons for adding, deleting replacing SVG's.
-
Add from file...
Select one ore more SVG files from the file system and add them to the back of the list in the order that they are read from the file system.
-
Replace...
Replace the currently selected SVG (row in the grid) with an SVG file from the file system.
-
Add
Adds a temporary SVG to the back of the list, which you can than alter by editing the SVG content or replacing it with an SVG file from the file system.
-
Insert
Inserts a temporary SVG before the selected row in the grid.
-
Delete
Delete the currently selected SVG (row in the grid).
-
Clear
Clears all SVG, Style and image data from SVG image list.
-
-
Template settings
Below the row of buttons, there is a drop-down box with a number of template settings. The templates apply settings to properties for a number of use cases.
-
Tab "Bitmaps"
This tab contains most of the properties of the TSVG2BaseImageList.
The "Width" and the "Height" represent the dimensions of the image in the lowest resolution
The "Color depth" is only present in the VCL version, de default is cd32Bit, which enables transparency with an alpha channel.
Also only on the VCL version is the "Masked" and "Back color" options, to create old style transparency by masking.
The "Scaled" property is present on all image lists, but for VCL this only has a function for Delphi 10.3 and higher and for FPC/Lazarus for version 1.9 and higher. Previous versions do not support scaling, but work-arounds are possible.
In case of scaling, the FMX and FPC/Lazarus versions need to have resolutions defined. Resolutions can be defined for the VCL version also, but alternatively it can scale the images by re-rendering.
-
Tab "SVG"
This tab contains the properties of the currently selected TSVG2ListItem. Which represents a row in the grid.
You can edit the content of the SVG here, or change the name. The name is used for exporting images.

-
Tab "Styles"
On this tab, TSVGImageStyle items can be added, edited and deleted. The STVGImageStyle represents a column in the grid.
There are two ways to style an SVG. One way is to add an "Outer SVG" that encloses the original SVG and changes it, for example by applying a filter. There are a couple of presets that you can select from the combobox. The other way is to insert entities in the original SVG and supply different values in each style. An example of this can be found in section Example creating styles.

-
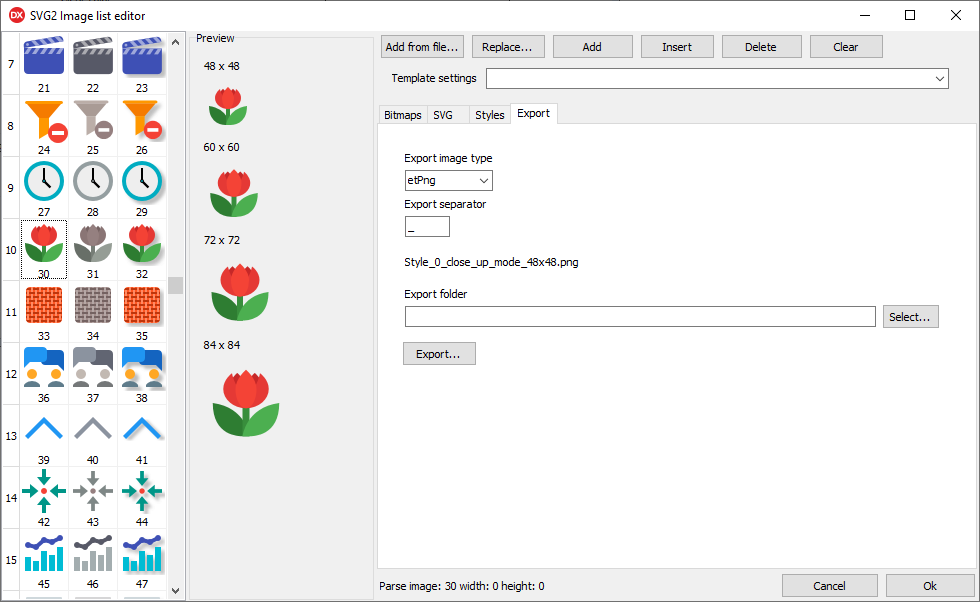
Tab "Export"
This tab contains settings for exporting all images to a folder in the file system.
TSVG2LinkedImageList component editor
There is also a component editor for the TSVG2LinkedImageList. It has the same "Bitmap" and "Export" tab as the TSVG2ImageList, but it lacks the "SVG" and "Styles". In stead it has a "Parent list" tab, where you can set the link to the parent TSVG2ImageList.
With the "Parent style index" you can select one of the styles that are defined in the parent TSVG2ImageList. If you set this to -1, all styles of the parent image list are used.
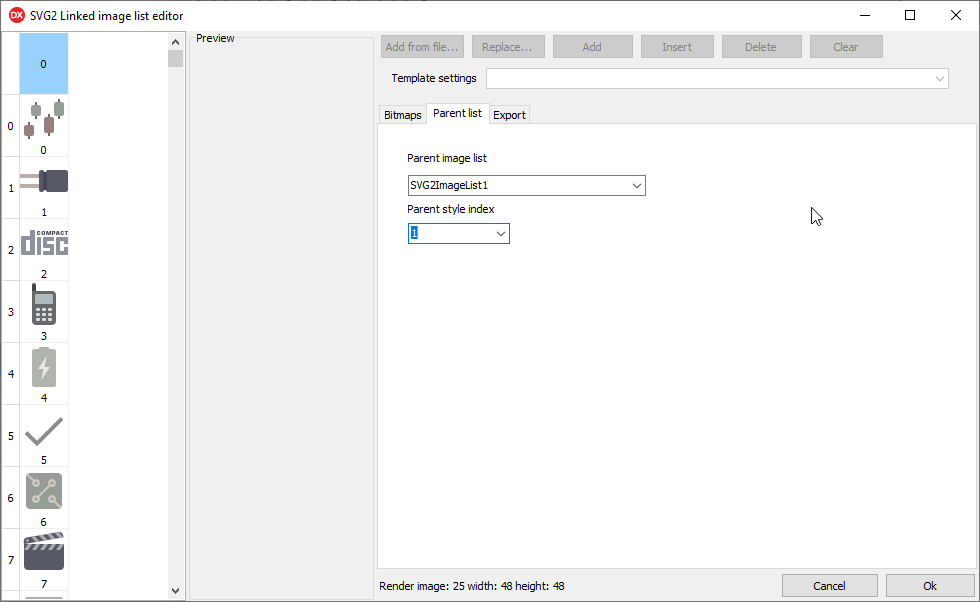
Example creating styles
An example for this is using a "Saturation" filter to create a "Disabled" version of an image. The outer SVG would look like this:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<defs>
<filter id="fltr_saturate">
<feColorMatrix in="SourceGraphic" type="saturate" values="0.20"/>
</filter>
</defs>
<g filter="url(#fltr_saturate)">&cur_svg;</g>
</svg>
Here &cur_svg; is a special entity that the parser will replace with the SVG from the SVG list.
There are a couple of default outer SVG's defined that you can select and modify if you wish, or you can create your own outer SVG, as long as it contains the &cur_svg; entity and it is a valid SVG after substitution.
Entities added to the SVG
Another means of altering the SVG in order to create a different style is by using Entities in the SVG itself. Entities are often used to replace special characters in XML, for example the symbol "<" is replaced in XML by the entity "<". See for details on Entities over here.
When the parser encounters an Entity in the SVG, it will add it to the Entity list of all the Styles that are defined in the TSVG2ImageList. For each style a different value for the Entity can be entered.
For example, we have the following SVG (start.svg):
<svg version="1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 48 48" enable-background="new 0 0 48 48">
<path fill="#F44336" d="M38,42H10c-2.2,0-4-1.8-4-4V10c0-2.2,1.8-4,4-4h28c2.2,0,4,1.8,4,4v28C42,40.2,40.2,42,38,42z"/>
<polygon fill="#fff" points="31,24 20,16 20,32"/>
</svg>
We want to create different styles by changing the colour, so we add a DTD and within that an Entity for the fill attribute:
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1 Basic//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11-basic.dtd" [
<!ENTITY fill_color "#F44336">
]>
<svg version="1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 48 48" enable-background="new 0 0 48 48">
<path fill="&fill_color;" d="M38,42H10c-2.2,0-4-1.8-4-4V10c0-2.2,1.8-4,4-4h28c2.2,0,4,1.8,4,4v28C42,40.2,40.2,42,38,42z"/>
<polygon fill="#fff" points="31,24 20,16 20,32"/>
</svg>
On parsing the entity "fill-color" will be added to the Entity list of all styles. On each style you can now set a different value.
The image below shows some other things that can be done, for example replacing a transformation value or a complete element with an entity.

The SVG used for the rotation example:
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1 Basic//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11-basic.dtd" [
<!ENTITY rotation "0">
]>
<svg version="1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 48 48" enable-background="new 0 0 48 48">
<path fill="#F44336" d="M38,42H10c-2.2,0-4-1.8-4-4V10c0-2.2,1.8-4,4-4h28c2.2,0,4,1.8,4,4v28C42,40.2,40.2,42,38,42z"/>
<polygon transform="rotate(&rotation;, 24, 24)" fill="#fff" points="31,24 20,16 20,32"/>
</svg>
The SVG used for the replaced element example:
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1 Basic//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11-basic.dtd" [
<!ENTITY shape "<polygon fill='#fff' points='31,24 20,16 20,32'/>">
]>
<svg version="1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 48 48" enable-background="new 0 0 48 48">
<path fill="#F44336" d="M38,42H10c-2.2,0-4-1.8-4-4V10c0-2.2,1.8-4,4-4h28c2.2,0,4,1.8,4,4v28C42,40.2,40.2,42,38,42z"/>
&shape;
</svg>
Example transparency on VCL and work-around in case of non-themed user interface
In VCL, the "Color depth" controls if the bitmaps in the list will support transparency. To enable transparency this must be set to "cd32bit" and the "Clear color" must be set to "clNone". However:
Windows only supports transparency on controls if runtime themes are enabled.
For example, in the following project the "Color depth" is set to "cd32bit" and the "Clear color" is set to "clNone".
If runtime themes are enabled, this will result in transparent images on the toolbar.
If runtime themes are disabled, in the application manifest or in the Windows OS settings, the background of the controls will become black.
A work around for this problem is to detect if runtime themes are enabled when the application starts and if not, to set the "Color depth" of the image list to "cd24" bit and the "ClearColor" equal to the controls background color, for example:
uses
Vcl.Themes;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
if not StyleServices.Enabled then
begin
SVG2ImageList1.BeginUpdate;
try
SVG2ImageList1.ClearColor := clBtnFace;
SVG2ImageList1.ColorDepth := cd24Bit;
finally
SVG2ImageList1.EndUpdate;
end;
end else begin
SVG2ImageList1.BeginUpdate;
try
SVG2ImageList1.ClearColor := clNone;
SVG2ImageList1.ColorDepth := cd32Bit;
finally
SVG2ImageList1.EndUpdate;
end;
end;
end;
After this, the images will have the following appearance in a non-themed application.
Example scaling
An example how to set up the image list for scaling can be found in the VCL demo viewer for Delphi 10.3.
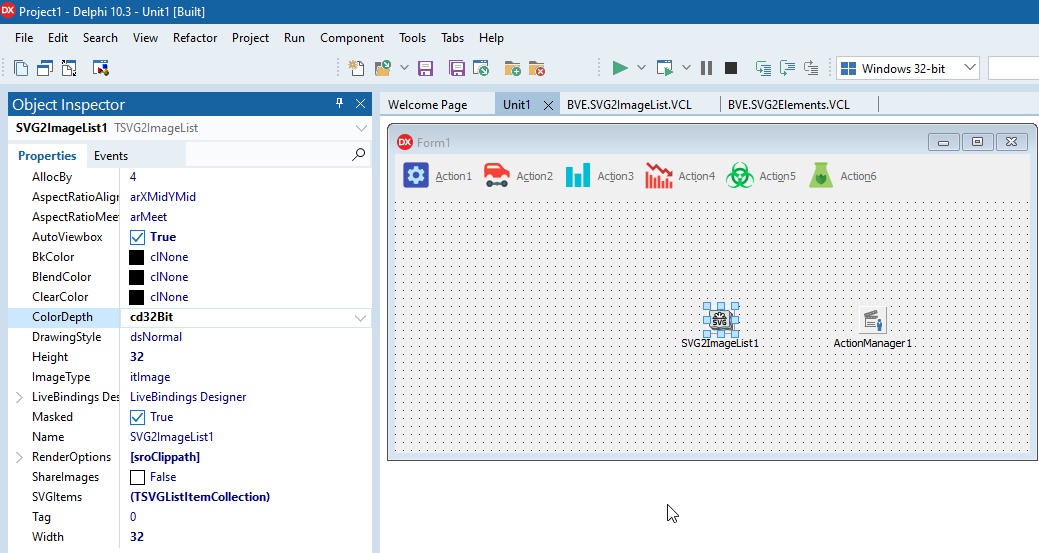
There is one SVGImageList1 component, that has two styles, style 0 with plain images and style 1 with disabled images using a saturation filter. There are two linked image lists, "ilNormal" is linked two style 0 of the SVGImageList1 and "ilDisabled" is linked to style 1 of SVGImageList1.
The "DisabledImages" property of the ActionManager1 component is set to "ilDisabled" and the "Images" property is set to "ilNormal".

The properties of the image lists are set up as folows:
| SVG2ImageList1 | ilNormal | ilDisabled | |
ParentImageList |
SVG2ImageList1 | SVG2ImageList1 | |
ParentStyleIndex |
0 | 1 | |
Scaled |
False | True | True |
ScalingKind |
skReRender | skReRender |
Monitor scale is set to 100%
Monitor scale is set to 125%
The scaling kind is set to "skReRender", so when scaling occurs, all images in the image lists that have the "Scaled" property set to "True" will be re-rendered. It is also possible to create the images beforehand. It that case the image list properties must be set up as follows:
| SVG2ImageList1 | ilNormal | ilDisabled | |
ParentImageList |
SVG2ImageList1 | SVG2ImageList1 | |
ParentStyleIndex |
0 | 1 | |
Scaled |
False | True | True |
ScalingKind |
skBestFitFromResolution | skBestFitFromResolution | |
Resolutions |
24 30 36 48 |
skBestFitFromResolution | skBestFitFromResolution |
In the VCL version the resolutions are kept within the main SVG2ImageList1 and are defined by the width in pixels of the images. In this example they are chosen as to be 100% 125% 150% and 200% of the base image width. Maybe you can do with less resolutions, this is something you have to try out.
The FPC/Lazarus viewer has a SVG2ImageList1 component on which three styles are defined. Linked image list "ilNormal" links to style 0, linked image list "liDisabled" is linked to style 1 using a saturation filter, and linked image list "ilHot" links to style 2 using a drop shadow filter.
The "Images" property of the toolbar is set to "ilNormal", the "DisabledImages" is set to "ilDisabled" and "HotImages" is set to "ilHot".
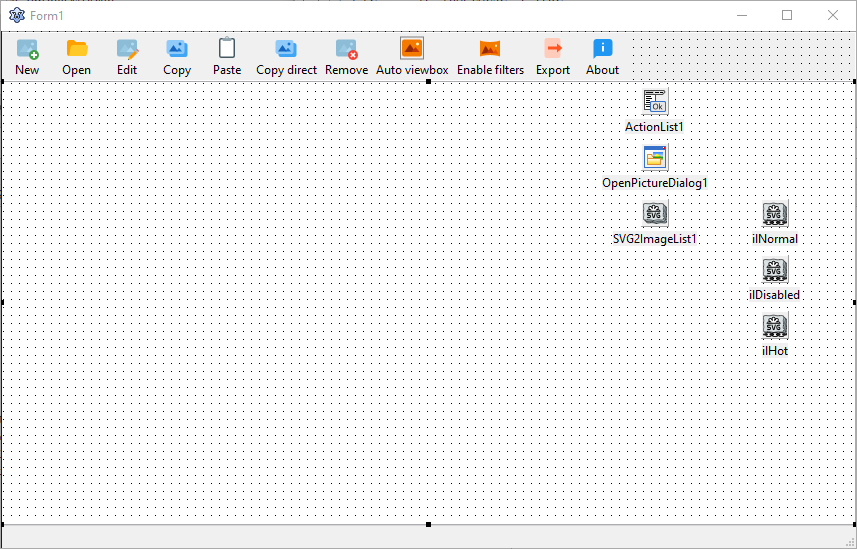
The properties for scaling on the image lists are set up as follows:
| SVG2ImageList1 | ilNormal | ilDisabled | ilHot | |
ParentImageList |
SVG2ImageList1 | SVG2ImageList1 | SVG2ImageList1 | |
ParentStyleIndex |
0 | 1 | 2 | |
Scaled |
False | True | True | True |
Resolutions |
24 30 36 48 |
24 30 36 48 |
24 30 36 48 |
There is no "ScalingKind" property for the FMX/Lazarus SVG image list, an image will be selected from the resolutions that best fit the image width needed for the linked control. If not an exact match can be found, than the system will try to find a larger resolution and than make it smaller by resampling it to the right size.
For the FMX version there is also no "ScalingKind" property, there is also no "Scaled" property because Delphi FMX has scaling build into the core of all controls by default. In the FMX TImageList is a multi resolution bitmap. Again all resolutions you are likely to need in your application, must be defined beforehand. The SVG image list will render the images on all layers of the multi resolution bitmap.
The FMX viewer demo application has a SVG2ImageList1 component for the application icons. Delphi FMX has no separate "DisabledImages" property on toolbars or menu's, so the styling functionality of the TSVG2Imagelist is not used and also no linked image lists are needed.

The scaling for the SVG2ImageList1 component is set up as follows:
| SVG2ImageList1 | |
Resolutions |
32 48 |
TSVG2BaseImageList
| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | Vcl.Controls.TImageList |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TCustomImageList |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | TCustomImageList |
Description
TSVG2BaseImageList is the parent class for TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImageList.
Properties
-
AutoViewbox: BooleanThis applies an AutoViewbox to all SVG's in the list on rendering.
See AutoViewbox in common properties.
-
AspectRatioAlign: TSVGAspectRatioAlignSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
AspectRatioMeetOrSlice: TSVGAspectRatioMeetOrSliceSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
BkColor: TColorVCL only
In case of masking, the "BkColor" represents the colour which is made transparent.
-
ClearColor: TColorBefore rendering an SVG, the target bitmap is cleared. The colour used for clearing is defined with "ClearColor". "clNone" in combination with "ColorDepth" of 32bit will result in a transparent background. "clNone" with any other "ColorDepth" will result in a black background.
-
ColorDepth: TColorDepthVCL only
This sets the pixel format for for the images in de list. The default is cd32bit, that is a pixel format that supports transparency with alpha. The SVG packaged creates 32bit images by default, so if you select another "ColorDepth" than 32bit, the system will need to do an extra conversion. The FMX and FPC/Lazarus image list only supports 32bit images, so this option is not available.
-
ExportFolder: stringProperty used by method "SaveImagesToExportFolder", it defines the folder where exported images will be saved to.
-
ExportImageType: TSVGExportImageTypeProperty used by method "SaveImagesToExportFolder", it defines image type that the images are converted to when exported to file or stream: etBmp, etJpg, etPng, etIco or etSvg. etIco is not supported in the FMX version.
-
ExportSeparator: stringProperty used by method "SaveImagesToExportFolder". The exported images must have a file name. The file name consists of a number of parts, the parts are separated with the text you set with ExportSeparator.
The parts of the file name are the following:
- StyleName
- SVGName
-
Resolution
The resolution is named using Width and Height, for example "48x48"
This is not used for icons, because the resolutions are embedded in the icon file. This is also not uses for SVG files.
-
The text "Mask"
This is for the mask version of an image. These are only created if "Masked" property of the image list is checked and not for icons because for icons the mask is embedded in the icon file and also not for SVG files.
-
Height: integerThe Height of the images in the image list in the lowest resolution.
-
Masked: BooleanVCL only
Before 32bit images where commonplace, masks where used to make certain areas of an image transparent. A mask can make parts of an image completely transparent or completely opaque, nothing in between. The VCL image lists still supports this, the FPC/Lazarus and FMX version does not. By checking "Masked" the TSVG2Imagelist will create an additional bit mask for each image in the list. Masking does not work with 32bit images.
-
Scaled: BooleanVCL and FPC/Lazarus
From Delphi 10.3 the image list is notified when the DPI setting is changed of it's owner form, with the "Scaled" property you can switch this behaviour on or off. If on, the image list will change the "Width" and "Height" properties of the images and this will either trigger a re-render of all images if "Scaling kind" is set to "Re-render", or a selection of an other resolution, if property "Scaling kind" is set to "From resolutions". In the last case, if no resolution is found with the exact image width needed, the image is stretched, so may lose some quality.
FPC/Lazarus supports multi-resolutions in the image list from version 1.9 onwards, if you check "Scaled" this will enable multiple resolutions. It works differently than Delphi. Controls send an extra parameter "ImageWidth" to the image list. With this the most appropriate resolution is selected. Again, if no exact match is found, the image will be stretched. Due to the architecture of the FPC/Lazarus image list in does not allow for re-rendering but only resolution selection, so it has no "Scaling kind" property.
Earlier versions of Delphi or FPC/Lazarus does not support the Scaling property.
-
ScalingKind: TSVGScalingKindVCL only
In case of VCL, this property controls the behaviour when scaling the image list. In case of "Re-render" all images will be re-rendered on scaling, in case of "From resolutions", a best fitting resolution from the resolution list is selected. However if the image of the selected resolution does not fit the target size, it is stretched. Selecting an image from an already available resolution is faster then re-rendering, but if an image needs to be stretched also, it will lose in quality.
-
SVGCount: integerThe number of SVG's in the list.
-
SVGItem[const aIndex: Integer]: TSVGListItemReturns the TSVGListItem collection item indicated by "aIndex" containing the SVG properties.
-
SVGStyleCount: IntegerThe number of Style's in the list.
-
SVGStyleItem[const aIndex: Integer]: TSVGImageStyleReturns the TSVGImageStyle collection item indicated by "aIndex" containing the Style properties.
-
RenderOptions: TSVGRenderOptions"Clippaths" and "Filters" use extra resources so you have the option of disabling them. By default these are enabled, if you want to uses filters in a style, you need to include "sroFilters" in the "RenderOptions". "sroEvents" has no effect on the SVG image list.
-
RenderQuality: TSVGBufferQualityVCL and FPC/Lazarus
The difference between "High performance" and "High quality" is that "High quality" will create anti-aliased images with smooth edges and "High performance" creates non anti-aliased images with pixelated edges. Anti-aliased images don't work well in combination with a mask. Some render context implementations only support anti-aliased images.
-
ResolutionByIndex[const aIndex: Integer]: TSVGImageListResolutionVCL and FPC/Lazarus
Returns the TSVGImageListResolution object indicated by "aIndex" from the resolution list.
-
ResolutionCount: IntegerVCL and FPC/Lazarus
Returns the number of extra resolutions defined in the image list.
-
Width: integerThe Width of the images in the image list in the lowest resolution.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVG2BaseImageList.
-
procedure BeginUpdate; virtual;Increases the internal update counter. If the update counter is greater than zero, properties can be set without triggering a re-render of one or all images. This also prevents triggering the "OnChange" event.
-
procedure EndUpdate; virtual;Decreases the internal update counter. If the update couner reaches zero again, it will re-render any images that need to be updates an then will trigger the "OnChange" event.
-
procedure ChangeScale(M, D: Integer);VCL only
ChangeScale will perform scaling of the SVG image list, using the kind of scaling set by property "SkalingKind".
-
procedure Clear; virtual;Clears the SVG list, Style list and all images in all resolutions.
-
procedure Draw(aCanvas: TCanvas; aX, aY, aWidth, aIndex: Integer); overload;Draws the image indicated by "aIndex" to the supplied canvas at coordinates "aX" and "aY". If "aWidth" differs from the image list "Width", the procedure will either re-render the image or select one from the resolutions, depending on the setting of "ScalingKind".
-
function ExportNameFormat(const aIndex, aResolutionIndex: Integer; const aMask: Boolean = FALSE): string;Creates a file name for the image indicated by "aIndex". If "aResolution" is a valid resolution but not zero, it includes the resolution in the file name. If "aMask" is TRUE, it includes the text "mask" in the file name. The sections are separated by the separator defined in property "ExportSeparator".
-
procedure GetGlyph(aIndexes: array of Integer; aBitmap: TBitmap);Assembles a glyph in the supplied bitmap, using the images supplied with the "aIndexes" array. Usage:
ImageList1.GetGlyph([0, 1, 2, 3], BitBtn1.Glyph);
BitBtn1.NumGlyphs := 4; -
function CreateIcon(const aIndex: Integer): TIcon;VCL and FPC/Lazarus
Creates a multi-layered Windows icon. The layers are defined by the resolutions.
-
procedure ParseSVG(const aIndex: Integer; aSVGRoot: ISVGRoot);Parses the SVG that produces the image indicated with "aIndex" and creates a rendering tree in aSVGRoot.
-
procedure RecreateImages; virtual;Recreates all images in all resolutions.
-
procedure SaveImagesToExportFolder;Save all images as specified by the export settings ExportFolder, ExportImageType and ExportSeparator.
When images are exported, they are re-parsed and re-rendered. The native format after rendering is a 32bit bitmap. Next they are converted to the format set by the EportImageType:
-
Bitmap (etBmp)
VCL
The pixel format of bitmaps of the VCL image list can be set with the "ColorDepth" property. The exported bitmap images will be converted to the pixel format indicated by "ColorDepth". If "Masked" is checked, a mask version of the image is exported as well.
FMX and FPC/Lazarus
The FPC/Lazarus image list only supports 32bit bitmaps.
-
JPEG (etJpg)
The SVG library uses the JPEG library that comes with Delphi and FPC/Lazarus to convert images to JPEG format.
-
Portable network graphic (etPng)
The SVG library uses the Png library that comes with Delphi and FPC/Lazarus to convert images to Png format.
-
Windows icon (etIco)
VCL
Procedure "SVGCreateIcon" in unit "BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL" is used to create Windows icons. If "Masked" is checked, than all layers of the icon will be of bitmap format, if "Masked" is not checked than all layers will be of Png format.
FPC/Lazarus
The SVG library uses FPC/Lazarus native software to convert images to Windows icon format. Resolutions smaller than 255 pixels width or height will create a layer of bitmap, higher resolutions will create a Png layer.
-
Scalable Vector Graphic (etSvg)
If you export images in SVG format, no parsing or rendering is needed but all Entities will be substituted according with the Style settings.
-
-
procedure SaveImageToFile(const aFilename: string; const aIndex: Integer; const aWidth, aHeight: Integer; const aMask: Boolean = FALSE);Save an image indicated with "aIndex" to file. The format of the exported image is determined by the file extension. The image is re-parsed and re-rendered to the given "aWidth" and "aHeight". In case of a multi-layered format like ".ico", "aWidth" and "aHeight" are ignored and the layers will be created according to the resolutions of the SVG image list. If "aMask" is TRUE, the a masked version of the image is saved.
-
procedure SaveImageToStream(aStream: TStream; const aType: TSVGExportImageType; const aIndex: Integer; const aWidth, aHeight: Integer; const aMask: Boolean = FALSE);Save an image indicated with "aIndex" to a stream. The format of the exported image must be given in aType. The image is re-parsed and re-rendered to the given "aWidth" and "aHeight". In case of a multi-layered format like ".ico", "aWidth" and "aHeight" are ignored and the layers will be created according to the resolutions of the SVG image list. If "aMask" is TRUE, the a masked version of the image is saved.
-
procedure SaveSVGToStream(const aIndex: Integer; aStream: TStream);Save the SVG that produces the image indicated with "aIndex" to a stream.
Events
-
OnChange: TNotifyEventOccurs when a property of the image list changes.
-
OnDrawItem: TSVGItemDrawEventOccurs when an image of the list is drawn.
-
OnProgress: TSVGImageListProgressOccurs when an item is parsed, rendered or resampled. Its usage is for indicating progress back to the user interface.
TSVGListItem
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | TCollectionItem TSVGBaseListItem |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TCollectionItem TSVGBaseListItem |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | TCollectionItem |
Description
TSVGListItem represents one SVG in the collection of SVG's in TSVG2ImageList.
Properties
-
IsEmpty: BooleanReturns TRUE if the SVG string list is empty.
-
SVG: TStringsA string list containing the SVG definition. A change of the string list will trigger a re-render for all images associated with the SVG.
-
SVGName: stringA name for the SVG, used when exporting images.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVGListItem.
TSVGImageStyle
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | TCollectionItem TSVGBaseListItem |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TCollectionItem TSVGBaseListItem |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | TCollectionItem |
Description
TSVGImageStyle represents one style item in the collection of style items in a TSVG2ImageList. The style item has properties to modify SVG's to create a extra set of images, for example to create a "Disabled" version of the images.
Different styles are created using the XML functionality of "Entities". XML entities are a way of representing an item of data within an XML document, instead of using the data itself.
An entity can be referred to in XML by the Entity name preceded with a "&" and followed by a ";".
Properties
-
EntityNames: TStringsA list of "Entity" names that are encountered during parsing of the SVG's.
-
EntityValues: TStringsA list of "Entity" values. Initially these have the value as defined in the DTD section of the SVG, but the values may be altered.
-
OuterSVG: TStringsAn enclosing SVG definition that embeds the SVG from the image list. The enclosing SVG can for example be used to apply an filter or effect on the SVG it encloses. The enclosed SVG from the list is referred to by a reserved entity name &cur_svg;.
-
OuterSVGType: TSVGOuterSVGTypeA number of pre-sets for the OuterSVG:
-
ostNone
No styling is applied.
-
ostCustom
A custom setting for the OuterSVG.
-
ostOpacity
Applies an opacity to the SVG making it transparent.
-
ostSaturate
Applies a saturation filter to the SVG to give a "Disabled" effect.
-
ostGlow
Applies a gaussian blur filter to the SVG.
-
ostDropShadow
Applies a drop shadow filter to the SVG.
-
-
StyleName: stringA name for the Style, used when exporting images.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVGImageStyle.
TSVGImageListResolution
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | System.Classes.TPersistent |
| Fpc | For FPC/Lazarus version 1.9 and up TCustomImageListResolution is used. | ||
| Fmx | Delphi XE8 and higher uses a multi resolution bitmap. | ||
Description
In VCL the TSVGImageListResolution is basically an extra image list within an image list but with larger images. The size of the images is defined by the "Width", the height of the images is calculated so that it is scaled proportionally.
Each resolution is one big data block of image count * image width * image height * 4 bytes. The extra resolutions can be used for DPI scaling, another use is for creating multi-layered images, for example icons.
In the VCL SVG image list, the type of scaling is controlled by the "ScalingKind" property, if it is set to "Re-render", than all images are re-rendered if scaling occurs and the extra resolutions are not needed, if the SVG's are very complex and it rendering takes a long time, you can set "ScalingKind" to "From resolutions". The system will then select a resolution that has images of the correct size or slightly larger and if so, resample the image.
The FPC/Lazarus image list supports scaling from version 1.9 onwards. It is basically a collection of image lists where each TCustomImageListResolution represents an image list with a different size of images. It's implementation does not allow for re-rendering of images, so if you need scaling, the extra resolutions must be defined always.
Properties
-
Count: IntegerReturns the number of images in the resolution.
-
Height: IntegerReturns the height of images in the resolution.
-
Width: IntegerReturns the width of images in the resolution.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVGImageListResolution.
-
procedure Clear;Clears the images of the resolution.
-
function GetBitmap(const aIndex: Integer; aImage: TBitmap): Boolean;Copies the image indicated by "aIndex" to the supplied bitmap.
-
procedure Draw(aRC: ISVGRenderContext; const aIndex, aX, aY, aWidth, aHeight: Integer; const aOpacity: TSVGFloat); overload; virtual;Draws the image indicated by "aIndex" to the supplied render context at coordinates "aX" and "aY". The image is stretched to "aWidth" and "aHeight" if its size differs. "aOpacity" can be 1.0, fully opaque, to 0.0 fully transparent.
-
procedure Draw(aCanvas: TCanvas; const aIndex, aX, aY, aWidth, aHeight: Integer); overload; virtual;Draws the image indicated by "aIndex" to the supplied canvas at coordinates "aX" and "aY". The image is stretched to "aWidth" and "aHeight" if its size differs.
TSVG2ImageList

VCL, FMX, FPC/Lazarus
| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | Vcl.Controls.TImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomImageList |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TCustomImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomImageList |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | FMX.ImgList.TCustomImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomImageList |
Description
The TSVG2ImageList keeps the collection of SVG's and Styles.
Properties
-
SVGItems: TSVGListItemCollectionA collection of TSVGListItem objects.
-
SVGStyles: TSVGImageStyleCollectionA collection of TSVGImageStyle objects.
Methods
-
procedure SetTemplate(const aTemplateID: Integer);The SetTemplate method applies settings to properties for a number of use cases.
Because the Delphi VCL image list has a different implementation for pixel formats, masking and DPI scaling than the FPC/Lazarus image list, there are different template options available for VCL and FPC/Lazarus.
Template settings for VCL
The VCL image list supports different pixel formats through "colour depth", masking and DPI scaling from version 10.3 onwards.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_32BIT_NORMAL_DPI_RERENDER32bit transparent, normal, re-render on DPI change
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There is no special style defined. The images will be re-rendered on DPI scaling, so there are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_32BIT_DISABLED_DPI_RERENDER32bit transparent, disabled, re-render on DPI change
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. Using a style a saturation filter is applied to the SVG to create a disabled affect. The images will be re-rendered on DPI scaling, so there are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_CENTRAL_32BIT_NORMAL_AND_DISABLED_DPI_RERENDER32bit transparent, normal and disabled, re-render on DPI change
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There are two styles, one normal, one disabled using a saturation filter. The images will be re-rendered on DPI scaling, so there are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_CENTRAL_32BIT_NORMAL_AND_DISABLED_DPI_PRERENDERED32bit transparent, normal and disabled, best fitting resolution on DPI change
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There are two styles, one normal, one disabled using a saturation filter. Extra resolutions are added with 125%, 150%, 175% and 200% of the Width and Height settings. On DPI scaling, the image will be selected from the best fitting resolution.
-
SVGILT_WIN10_ICON_32BITWindows icons with 32bit bitmap images
This will set up the image list for the creation of multi layered Windows icons. The layers of the icon will be uncompressed 32bit bitmaps with a mask.
-
SVGILT_WIN10_ICON_PNGWindows icons with Png images
This will set up the image list for the creation of multi layered Windows icons. The layers of the icon will be compressed using Png format.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_24BIT_MASKED_NORMAL_DPI_RERENDER24bit masked, normal, re-render on DPI change (legacy)
This will set up the image list for 24bit images using a mask.
Template settings for FPC/Lazarus
The FPC/Lazarus image list supports only 32bit images, no masking and DPI scaling from version 1.9 onwards. For DPI scaling you have to define extra resolutions, re-rendering on DPI scaling is not supported. So there are less template settings for FPC/Lazarus.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_NORMALNormal
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There is no special style defined. There are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_DISABLEDDisabled
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. Using a style a saturation filter is applied to the SVG to create a disabled affect. There are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_CENTRAL_NORMAL_AND_DISABLEDNormal and disabled
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There are two styles, one normal, one disabled using a saturation filter. There are no extra resolutions defined.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_NORMAL_SCALEDNormal, scaled (Laz version 1.9 and higher)
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There is no special style defined. Extra resolutions are added with 125%, 150%, 175% and 200% of the Width and Height settings. On DPI scaling, the image will be selected from the best fitting resolution.
-
SVGILT_STANDALONE_DISABLED_SCALEDDisabled, scaled (Laz version 1.9 and higher)
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. Using a style a saturation filter is applied to the SVG to create a disabled affect. Extra resolutions are added with 125%, 150%, 175% and 200% of the Width and Height settings. On DPI scaling, the image will be selected from the best fitting resolution.
-
SVGILT_CENTRAL_NORMAL_AND_DISABLED_SCALEDNormal and disabled, scaled (Laz version 1.9 and higher)
This will set up the image list with 32bit images supporting transparency with alpha channel. There are two styles, one normal, one disabled using a saturation filter. Extra resolutions are added with 125%, 150%, 175% and 200% of the Width and Height settings. On DPI scaling, the image will be selected from the best fitting resolution.
-
SVGILT_WIN10_ICONWindows icons (Laz version 1.9 and higher)
This will set up the image list for the creation of multi layered Windows icons. The layers with Width or Height greater or equal than 255 will will be uncompressed to Png format.
-
-
function ResolutionAdd(const aWidth: Integer): Integer;Add a resolution layer to the image list. "aWidth" sets the width of the images in the list, the height of the images in the resolution is calculated by proportional scaling.
-
procedure ResolutionDelete(const aIndex: Integer);Delete a resolution layer from the image list.
-
procedure ResolutionsClear;Delete all resolution layers from the image list.
-
procedure ResolutionsRegister(const aResolutionWidths: array of Integer);Adds a number of resolution layers to the image list, defined by the "aResolutionWidths" array. Existing resolutions will be cleared first.
-
function AddSVG(const aValue: string; const aName: string = ''): integer;Adds an SVG to the list.
-
procedure DeleteSVG(const aSVGIndex: integer);Deletes an SVG from the list.
-
function InsertSVG(const aSVGIndex: integer; const aValue: string; const aName: string = ''): integer;Insert an SVG to the list an position aSVGIndex.
-
procedure ReplaceSVG(const aSVGIndex: integer; const aValue: string; const aName: string = '');Replaces an SVG in the list.
TSVG2LinkedImageList

VCL, FMX, FPC/Lazarus
| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | Vcl.Controls.TImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomLinkedImageList |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TCustomImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomLinkedImageList |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | FMX.ImgList.TCustomImageList TSVG2BaseImageList TSVG2CustomLinkedImageList |
Description
The TSVG2LinkedImageList is almost the same as as a TSVG2ImageList. It has its own list of images and most of TSVG2ImageList properties are present in TSVG2LinkedImageList as well, the main difference is that it does not contain any SVG or Style data, but uses these from the TSVG2ImageList it is linked to.
This makes it possible to centralize the SVG and Style data in one place and use TSVG2LinkedImageList as "agents" on forms, that are set up for the needs of that particular form. Something like the new TVirtualImageList and TImageCollection in Delphi 10.3
Properties
The TSVG2LinkedImageList has two properties for linking with a TSVG2ImageList:
-
ParentImageList: TSVG2CustomImageListWith this property you set the TSVG2ImageList that contains the SVG and Style data to use.
-
ParentStyleIndex: IntegerWith ParentStyleIndex you can select which Style of ParentImageList to use. If you set this to -1, all styles of the ParentImageList will be included.
TSVG2Graphic
| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2Graphic.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2Graphic.VCL | Vcl.Graphics.TGraphic |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2Graphic.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2Graphic.FPC | TGraphic |
| Fmx | Not available | ||
Description
The TSVG2Graphic is a non-visible component. It is derived from TGraphic and so can be used as any other TGraphic derived classes (like TJPEGImage and TPngImage).
If you look at the initialization section of the BVE.SVG2Graphic.VCL.pas unit, you will see that the TSVG2Graphic is used to register the SVG file format.
initialization
// Register the file format for load/save dialog
TPicture.RegisterFileFormat('svg', 'Scalable Vector Graphics', TSVG2Graphic);
Because it is registered, the TOpenPictureDialog will recognize SVG files as a graphic format, and also you can load SVG files into the "Picture" property of Delphi's standard TImage control.
Properties
-
AspectRatioAlign: TSVGAspectRatioAlignSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
AspectRatioMeetOrSlice: TSVGAspectRatioMeetOrSliceSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
AutoViewbox: booleanSee AutoViewbox in common properties.
-
Bitmap: TBitmapSee Bitmap in common properties.
-
BufferQuality: TSVGBufferQualitySee BufferQuality in common properties.
-
ElementIndex: TStringsSee ElementIndex in common properties.
-
Filename: TFileNameSee Filename in common properties.
-
Iri: TSVGIriSee Iri in common properties.
-
NeedsParse: booleanSee NeedsParse in common properties.
-
NeedsRepaint: booleanSee NeedsRepaint in common properties.
-
RenderContextType: TSVGRenderContextTypeSee RenderContextType in common properties.
-
RenderOptions: TSVGRenderOptionsSee RenderOptions in common properties.
-
RootID: stringSee RootID in common properties.
-
Scale: TSVGFloatSee Scale in common properties.
-
SVG: TStringsSee SVG in common properties.
-
SVGRoot: ISVGRootSee SVGRoot in common properties.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVG2Graphic.
-
function DoMouseDown(const aButton: TMouseButton; const aShift: TShiftState; const aClientX, aClientY, aScreenX, aScreenY: single): boolean;A call to this method will create SVG mouse pointer events triggered from a mouse button down, if sroEvents is included in property RenderOptions.
-
function DoMouseMove(const aShift: TShiftState; const aClientX, aClientY, aScreenX, aScreenY: single): boolean;A call to this method will create SVG mouse pointer events triggered from a mouse move, if sroEvents is included in property RenderOptions.
-
function DoMouseUp(const aButton: TMouseButton; const aShift: TShiftState; const aClientX, aClientY, aScreenX, aScreenY: single): boolean;A call to this method will create SVG mouse pointer events triggered from a mouse button up, if sroEvents is included in property RenderOptions.
-
function ObjectAtPt(aPt: TPointF): ISVGObject;See ObjectAtPt in common methods.
-
procedure ParseSVG;See ParseSVG in common methods.
Events
-
OnAfterParse: TNotifyEventSee OnAfterParse in common events.
-
OnSVGEvent: TSVGEventSee OnSvgEvent in common events.
Examples
See the "OpenPicture" project in the Examples folder.
For an example how to use TSVGGraphic see Assign an SVG to a TSVG2Graphic object and assign to a standard TImage.
SVG Controls
The SVG controls TSVG2Control, TSVG2Image and TSVG2LinkedImage can be used to display and interact with a single SVG. They are all derived from TSVGBaseControl. The main difference is where the SVG is stored and with what defaults the controls are initialized.
| SVG source | AutoViewbox | Clipping | |
| TSVG2Control | From file From strings from a TSVG2Doc |
False | True |
| TSVG2Image | From file From strings |
True | False |
| TSVG2LinkedImage | From an imagelist | True | False |
The VCL version of the controls is derived from TGraphicControl. A TGraphicControl is rendered in the paint cycle of its parent TWinControl. As all VCL controls there will be some flicker if the control repaints itself, to avoid flicker you should set the "DoubleBuffered" property of the parent TWinControl to "True".
The FPC/Lazarus and FMX versions do not suffer from this flicker problem.
TSVG2BaseControl
| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2Control.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.VCL | Vcl.Controls.TGraphicControl |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2Control.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.FPC | TGraphicControl |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2Control.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.FMX | FMX.Controls.TControl |
Description
TSVG2BaseControl is the base class for the SVG controls.
All measuring, rendering and interaction is defined in TSVG2BaseControl. The derived SVG controls only add the source for the SVG.
Properties
-
AspectRatioAlign: TSVGAspectRatioAlignSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
AspectRatioMeetOrSlice: TSVGAspectRatioMeetOrSliceSee AspectRatioAlign in common properties.
-
AutoViewbox: booleanSee AutoViewbox in common properties.
-
Bitmap: TBitmapSee Bitmap in common properties.
-
BufferQuality: TSVGBufferQualityVCL, FPC only
See BufferQuality in common properties.
-
Clipping: booleanIf True, the bitmap buffer bounds are clipped to the canvas to prevent memory overflow on scaling. The drawback is that the SVG will need to be re-rendered every time the control is moved or scaled while clipped.
-
ContentBounds: TRectFThe calculated bounds of the SVG.
-
ElementIndex: TStringsSee ElementIndex in common properties.
-
Iri: TSVGIriSee Iri in common properties.
-
NeedsParse: booleanSee NeedsParse in common properties.
-
NeedsRepaint: booleanSee NeedsRepaint in common properties.
-
Padding: TPaddingControls where the buffer is painted within the control bounds by adding space around the edges.
-
RenderContextType: TSVGRenderContextTypeSee RenderContextType in common properties.
-
RenderOptions: TSVGRenderOptionsSee RenderOptions in common properties.
-
RootID: stringSee RootID in common properties.
-
Scale: TSVGFloatVCL, FPC only, Scale on FMX is inherited from TControl and has another meaning
See Scale in common properties.
-
SVGRoot: ISVGRootSee SVGRoot in common properties.
Methods
-
procedure Assign(Source: TPersistent); override;Copies settings from another TSVG2BaseControl.
-
procedure CalcSize; virtual;See CalcSize in common methods.
-
function ObjectAtPt(aPt : TPointF; const aIfHitTest: boolean = True): ISVGObject;See ObjectAtPt in common methods.
-
procedure ParseSVG;; virtual; abstract;See ParseSVG in common methods.
-
See Repaint in common methods.procedure Repaint; override;
Events
-
OnAfterParse: TNotifyEventSee OnAfterParse in common events.
-
OnPaint: TNotifyEventSee OnPaint in common events.
-
OnSVGEvent: TSVGEventSee OnSvgEvent in common events.
TSVG2Control

| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2Control.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.VCL | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomControl |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2Control.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.FPC | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomControl |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2Control.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2Control.FMX | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomControl |
Description
TSVG2Control is used for displaying and interacting with a single SVG. It inherits most of its properties, methods and events from TSVGBaseControl.
By default the control is clipped by the parent canvas and property "AutoViewBox" is False. The SVG can be read from file, stored in an internal TStringList object or read from a linked TSVG2Doc component.
Properties
-
Filename: TFileNameSee Filename in common properties.
-
SVG: TStringsSee SVG in common properties.
-
SVGDoc: ISVGDocAllows linking to a TSVGDoc component. If set, this will overrule the "Filename" and "SVG" properties.
TSVG2Image

| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2Image.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2Image.VCL | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomImage |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2Image.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2Image.FPC | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomImage |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2Image.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2Image.FMX | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomImage |
Description
The TSVG2Image control is also used for displaying and interacting with a single SVG. It inherits most of its properties, methods and events from TSVGBaseControl.
By default the control is not clipped to the parent canvas and "AutoViewBox" is True. The SVG can be read from file or stored in an internal TStringList object.
Properties
-
Filename: TFileNameSee Filename in common properties.
-
SVG: TStringsSee SVG in common properties.
TSVG2LinkedImage

| Source | Unit | Parent | |
| Vcl | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.VCL | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomLinkedImage |
| Fpc | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FPC | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomLinkedImage |
| Fmx | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX.pas | BVE.SVG2ImageList.FMX | TSVGBaseControl TSVG2CustomLinkedImage |
Description
The is the same as an TSVGImage only it reads its SVG from a TSVG2ImageList.
Properties
-
Images: TSVG2BaseImageListThe TSVG2ImageList that contains the SVG.
-
ImageIndex: integerThe index in the connected image list that specifies the SVG to use.
Common methods of the SVG components
-
procedure ParseSVG;Explicitly parse the SVG content specified by SVG or Filename and rebuild the "SVGRoot" object.
-
function ObjectAtPt(aPt : TPointF; const aIfHitTest: boolean = True): ISVGObject;Finds the element of type TSVGObject at the supplied user coordinates. If no element is found the function returns nil. Only TSVGObject elements that have the "Hittest" property set to TRUE are checked. Also, sroEvents must be included in the render options.
-
procedure CalcSize; virtual;Sets the bounds of the control to the size defined in the SVG graphic.
- Repaint>
procedure Repaint; override;Forces a repaint of the SVG.
Common properties of the SVG components
-
AspectRatioAlign: TSVGAspectRatioAlignAspectRatioMeetOrSlice: TSVGAspectRatioMeetOrSliceWith this you can control how the SVG image is aligned within the bounds of the control. The available settings are equivalent to those from the "preserveAspectRatio" attribute.
-
AutoViewbox: booleanIf set to TRUE This will automatically insert a viewBox into the outermost SVG element. It will set the preserveAspectRatio to XMidYMid, meet.
The result is that the SVG Image will always be nicely centered within the control. For some SVG images this is not needed because they already have a viewBox defined on the outermost SVG element.
It will be at the cost of some performance because the intrinsic size of the SVG image has to be calculated before rendering of the SVG image.
Image shows AutoViewbox set to FALSE and TRUE.
-
Bitmap: TBitmapThis property gives access to the internal bitmap buffer of the SVG component. You could use this to save a bitmap of the rendered SVG image to file.
This is not available on the TSVG2ImageList and TSVG2LinkedImage, but you can export bitmaps in the component editor of the image list.
-
BufferQuality: TSVGBufferQualityWith this property you can control the quality of the rendered SVG image, this only works for the render contexts based on Direct2D or GDI+, the others always render on the high quality setting.
Possible values are bqHighPerformance or bqHighQuality. In case of Deirect2D and GDI+ the high quality setting will result in anti-aliased images and high speed will not be anti-aliased.
-
ElementIndex: TStringsThe ElementIndex is a list of strings containing the element ids of the SVG image.
-
Filename: TFileNameFileName property you can use to specify the SVG file you want to parse and render.
-
Iri: TSVGIriThe Iri property returns a resource identifier structure build from the FileName and the RootID property.
-
NeedsParse: booleanThe NeedsParse property can be set to force parsing of the SVG content before the next paint.
-
NeedsRepaint: booleanThe NeedsRepaint property can be set to force a new render of the rendering tree before the next paint, if not set, the component will just paint the earlier rendered bitmap buffer to the canvas.
-
RenderContextType: TSVGRenderContextTypeReturns the render context type used for rendering.
-
RenderOptions: TSVGRenderOptionsWith the RenderOptions property you can set SVG functionality to include or exclude. This is functionality that would use a lot of resources so you have the option to exclude them.
Possible values are:
- sroFilters (default off): include filter functionality. Filters usually are CPU intensive and need buffers
- sroClippath (default on): include clippath functionality. Clippath is implemented as an alpha mask and needs a buffer
- sroEvents (default off): include SVG event functionality and enables mousepointer events. For this an extra data structure (TSVGObjectState tree) is build on rendering with bounds information of each visible element.

Image showing RenderOptions = [sroClippath] and RenderOptions = [sroFilters,sroClippath]
-
RootID: stringIf you want to render only a subset of an SVG image, you can set this property with the element id from which to start. If you leave this empty, then rendering will start on the outermost svg element of the SVG content.
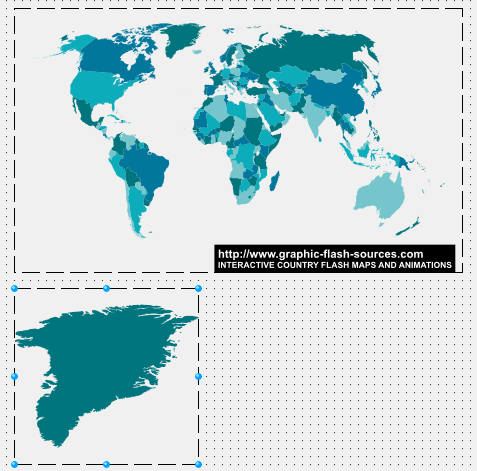
Image showing a map of the world, and another TSVG2Control using the same SVG graphic but with RootID set to "region139.GREENLAND".
-
Scale: TSVGFloatThe scale factor for the control. This will be used for DPI-scaling for example.
-
SVG: TStringsThe SVG property can be used to specify a SVG file to render as strings, instead of using the FileName property. It also has a higher priority than the FileName property so if you specify a Filename as well as fill the SVG string with SVG content, then the SVG from the SVG property will be rendered.
The SVG content that is added to the SVG property will be saved in the .dfm or .fmx file, and will be build into your executable, so you don't need to supply your SVG content as separate files with your application.
-
SVGRoot: ISVGRootThe SVGRoot property gives access to the root of the rendering tree. So you could modify element properties or style directly in the rendering tree without parsing the SVG image.
After modifying rendering tree elements you should set NeedsRepaint to TRUE, to repaint the buffer.
Common events of the SVG components
-
OnPaint: TNotifyEventFires directly after the SVG content is painted on the canvas.
-
OnAfterParse: TNotifyEventFires directly after parsing and building of the rendering tree.
-
OnSVGEvent: TSVGEventIf you have set the sroEvents option in the "RenderingOptions" property, than the OnSVGEvent will fire when an SVG event occurs.
The event handler is defined like this:
TSVGEvent = procedure(Sender: TObject; aSVGRoot: ISVGRoot; aEvent: ISVGEvent; const aValue: string) of object;- Sender (TObject): the SVG control object
- aSVGRoot (ISVGRoot): interface to the rendering tree root
- aEvent (TSVGEvent): interface to the event object that is triggered
- aValue (string): the value of the svg event attribute in the svg document that is triggered
See the "Using mouse events" for an example how to use SVG events.
Technical design
The following section explains the design and architecture of the package.
Process flow
The purpose of the package is to transform raw SVG data into a something that can be used in an application. This could be a raster image, for example a bitmap in one or more different sizes and/or provide a structure for changing, animating or interacting with the SVG data.
Basically there are two processing stages:
- Parsing the input SVG data and producing a document object model (DOM) which is represented in the package by the ISVGRoot interface.
- Rendering the DOM to the output.
The input SVG data is basically text structured as XML in which the elements and attributes provide the instructions of how the graphic should be rendered.
The output will almost always be a raster image in the form of a in memory 32bit bitmap with alpha (transparency channel). The alpha can be premultiplied or not depending on the platform. The bitmap can be converted to PNG or JPG of something else and written to file.
Optionally the render stage can also output an "object state tree" represented by an ISVGObjectState interface. For every visible element of the DOM a corresponding object state is created. Because the object state contains the bounding boxes of all visible elements, we can determine de elements behind every pixel in the raster image. This in turn is used to process mouse pointer events.
The renderer can also output EMS files. EMS files consist of GDI+ instructions and can only be produces by the GDI+ render context.
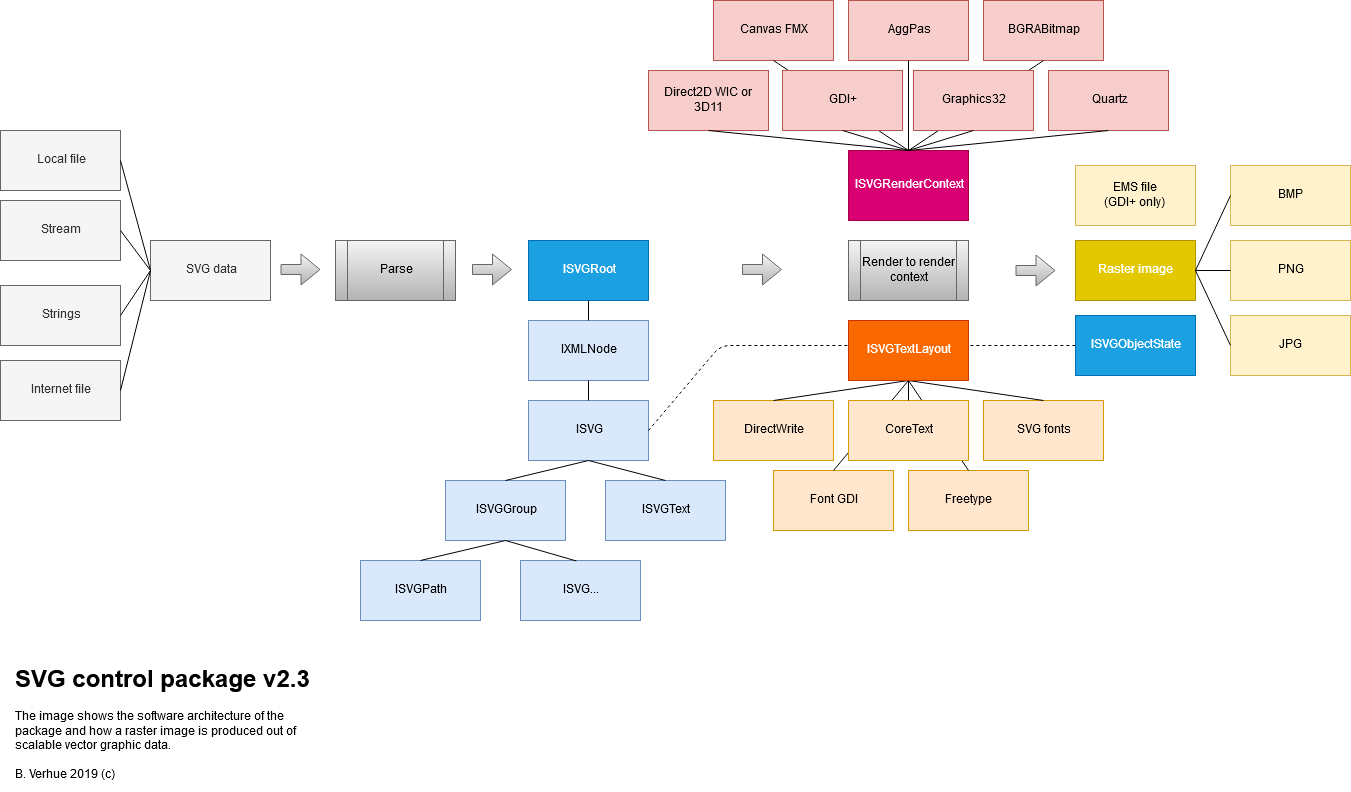
Zooming in on the rendering process, this can be divided into two sub processes:
- Issuing drawing instructions to the render context
- Rasterization
Drawing instructions to the render context are similar to the drawing instructions you would give to the canvas: DrawRect, FillRect, DrawEllipse etc.
The ISVGRoot implementation has the capability to render itself to the render context, by issuing the render instructions in the correct order and if necessary apply transformations, rendering to intermediate buffers or loading external resources like referenced svg graphics or bitmaps. This is the core functionality provided by the package.
The rasterization is delegated to the render context implementation. An important part of this is drawing polygons often filled by a scan line algorithm, for which different render context implementations provide different solutions. The decision to delegate the rasterization to an external software package was made as to benefit from existing solutions and not to reinvent the wheel. These external software solutions are either already provided by the operating system (Direct2D, GDI+ for windows, Quartz for Mac) or are graphic packages developed by the Delphi FPC Lazarus community (Graphics32, Aggpas, BGRABitmap). Also this makes it easier to provide a multi platform SVG solution.
See section "Render Contexts" for a complete overview of available render contexts.
A similar approach is taken for fonts and the rendering of text. Rendering text for different languages can be very very complex, so the package provides interfaces to existing solutions from which you can choose: DirectWrite or GDI + Uniscribe for Windows, CoreText for Mac or Freetype if these are not available. An exception is SVG fonts. Officially SVG fonts are no longer supported by the SVG standard, but because they provide a platform independent solution for rendering text, the functionality is kept in the package.
The following diagram shows how text is rendered. The implementation of the ISVGTextLayout interface handles the conversion of text with style information to path data. The style information includes font family, font weight, font style and so on.
With this information a best fitting font is selected from the font source. This is a database of fonts implemented by the ISVGFontSource interface.
You can select the ISVGTextLayout implementation that you want to use with a "global define". For windows you can select DirectWrite or GDI fonts, for Mac you can select CoreText or you can select Freetype which is available for almost every operating system.
If you don't select a specific text layout implementation in the global defines, than only SVG fonts will be rendered.
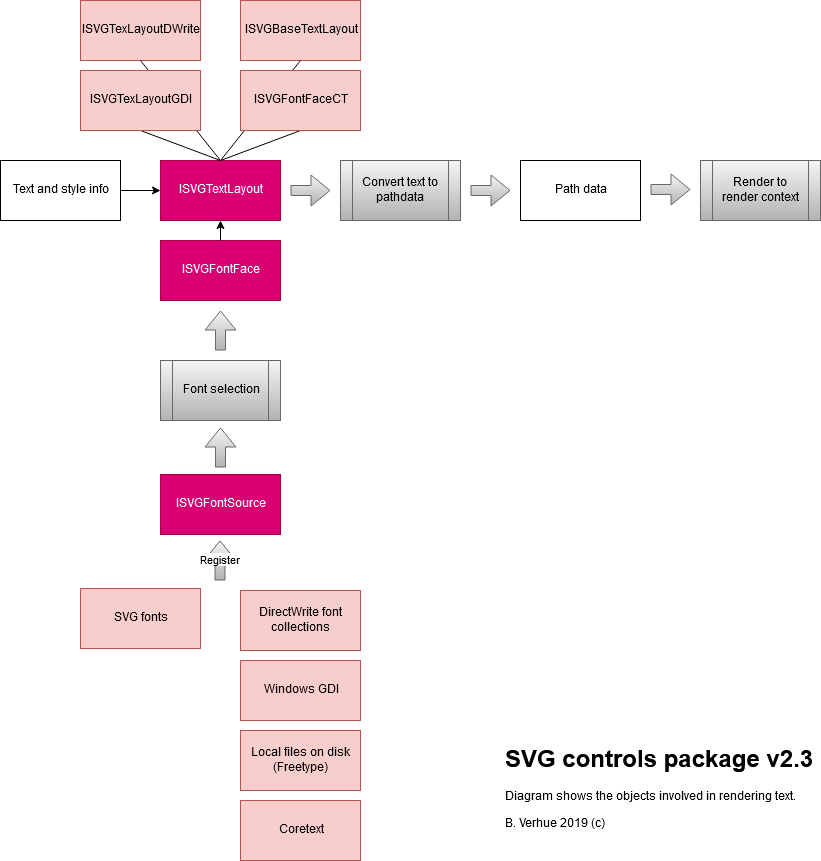
The RenderContext and TextLayout are independent of each other. So on Windows for example, you could use Graphics32 as the render context implementation and DirectWrite as the text layout implementation.
See section "Text layouts" for a complete overview of available options for rendering text.
Global defines
The package uses include files for setting global parameters using defines. These defines determine which render context is used, which text layout and a number of other settings.
There is one common include file,
CompilerSettings.inc on folder
Common and there is one include file for each platform:
ContextSettingsVCL.inc for VCL in folder
Common\Vcl,
ContextSettingsFMX.inc for Firemonkey in folder
Common\Fmx and
ContextSettingsFPC.inc" for FPC Lazarus in folder
Common\Fpc.
CompilerSettings.inc
Most defines in this file are switches for handling platform and Delphi version differences and you should not change these. There are a couple of defines that can be changed, these are listed in following table:
| Define | Meaning | Default setting |
|---|---|---|
| SVGInlining | This will cause some code to be inlined, which can speed up the software at the exspense of a larger executable. | On |
| SVGDEBUG | This will draw boxes around elements, and is used to debug the code. | Off |
| SVGD2Debug | This will set Direct2D in debug mode so Direct2D errors and messages are visible in the Delphi message panel. | Off |
| SVGProfiler | This will enable a build in profiler, sometimes used for development of the package. | Off |
| SVGInternetAccess | This will allow resources to be loaded from internet. For this Indy components will be compiled in the software and you might have to install libeay32.dll and ssleay32.dll for support for https. | Off |
ContextSettingsVCL.inc
The defines in this include file determine which render context implementation and which text layout implementation is used in Delphi VCL applications.
| Define | Meaning | Default setting |
|---|---|---|
| SVGDirect2d3D11 | This will include the Direct2D render context implementation, which renders to a DirectX device context. | Off |
| SVGDirect2dDWIC | This will include the Direct2D render context implementation, which renders to a WIC bitmap. | On |
| SVGGDIP | This will include the GDI+ render context implementation, which uses GDI+ for rendering. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGGraphics32 | This will include a render context based on the "Graphics32" library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGFontDirectWrite | This will include a text layout implementation based on DirectWrite, for using system fonts and text formatting. | On |
| SVGFontGDI | This will include a text layout implementation based on GDI and Uniscribe, for accessing system fonts and formatting text. | Off |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the Freetype text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. See "Freetype.org" for more info. | Off |
You are allowed to enable SVGDirect2d3D11, SVGDirect2dDWIC, SVGGDIP and SVGFontDirectWrite and SVGFontGDI all at the same time. In that case the system will select the render context and text layout at run time, out of the options available op target system.
For example you want to use Direct2D using WIC and if Direct2D is not available on the target system you want to use GDI+, you would enable both SVGDirect2dDWIC and SVGGDIP.
The system will try SVGDirect2d3D11 first if enabled, then SVGDirect2dDWIC and last SVGGDIP. The same for text layouts, it will first try SVGFontDirectWrite if enabled then SVGFontGDI.
ContextSettingsFMX.inc
The defines in this include file determine which render context implementation and which text layout implementation is used in Delphi Firemonkey (FMX) applications. Because Firemonkey can build to different operating system targets, there is a set of defines for each possible operating system.
| Define | Meaning | Default setting |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||
| SVGDirect2dDWIC | This will include the Direct2D render context implementation, which renders to a WIC bitmap. | Off |
| SVGGDIP | This will include the GDI+ render context implementation, which uses GDI+ for rendering. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGFMXCanvas | This will include a render context based on the default Firemonkey canvas. System fonts will also be accessed via the Firemonkey canvas. | On |
| SVGFontDirectWrite | This will include a text layout implementation based on DirectWrite, for using system fonts and text formatting. | Off |
| SVGFontGDI | This will include a text layout implementation based on GDI and Uniscribe, for accessing system fonts and formatting text. | Off |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the Freetype text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handeled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | Off |
| Apple OsX or iOS | ||
| SVGQUARTZ | This will include a context implementation based on Quartz. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. This is not tested on iOS. | Off |
| SVGFMXCanvas | This will include a render context based on the default Firemonkey canvas. System fonts will also be accessed via the Firemonkey canvas. | On |
| SVGFontCoreText | This will include a text layout implementation based on CoreText, for using system fonts and text formatting. | Off |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the Freetype text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handeled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | Off |
| All other operating systems | ||
| SVGFMXCanvas | This will include a render context based on the default Firemonkey canvas. System fonts will also be accessed via the Firemonkey canvas. | On |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the Freetype text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handeled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | Off |
ContextSettingsFPC.inc
The defines in this include file determine which render context implementation and which text layout implementation is used in FPC Lazarus applications. Again because FPC Lazarus can build to different operating system targets, there is a set of defines for each possible operating system.
| Define | Meaning | Default setting |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||
| SVGDirect2d3D11 | This will include the Direct2D render context implementation, which renders to a DirectX device context. | Off |
| SVGDirect2dDWIC | This will include the Direct2D render context implementation, which renders to a WIC bitmap. | On |
| SVGBGRABitmap | This will include a render context based on the "BGRABitmap" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGGraphics32 | This will include a render context based on the "Graphics32" library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGFontDirectWrite | This will include a text layout implementation based on DirectWrite, for using system fonts and text formatting. | On |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the "Freetype" text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | Off |
| Darwin | ||
| SVGQuartz | This will include a context implementation based on Quartz. | On |
| SVGBGRABitmap | This will include a render context based on the "BGRABitmap" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGGraphics32 | This will include a render context based on the "Graphics32" library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGFontCoreText | This will include a text layout implementation based on CoreText, for using system fonts and text formatting. | On |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the "Freetype" text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handeled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | Off |
| Linux | ||
| SVGBGRABitmap | This will include a render context based on the "BGRABitmap" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | On |
| SVGGraphics32 | This will include a render context based on the "Graphics32" library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGAGGRenderer | This will include a render context based on the "Modernised Anti Grain" graphics library. You need to download this library to be able to compile with this setting. | Off |
| SVGFreetype | This Includes the "Freetype" text layout implementation for accessing system fonts. Text formatting is handeled by the SVG control package. The freetype.dll is has to be available on the system. | On |
| Other operating systems have not been tested... | ||
Render contexts
There are a number of different render context implementations available in the package. Sometimes there is more than one render context available for an operating system, you can select the render context you want to use as explained in the previous section. The quality of the rendered image depends for a large part on the underlying graphics library of the selected render context.
Render contexts for Delphi
| Render context | Supported OS* | Graphics library | Platform | Quality | Rendering speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVG2ContextD2D | Windows 7 and higher | Direct2D | VCL, FMX | Very good, some minor issues withe the stroke-cap. | Very good |
| SVG2ContextGP | Windows XP and higher | GDI+ | VCL, FMX | Good, except the radial gradients | Very good |
| SVG2ContextQuartz | OsX, iOS | Quartz | FMX | Good, radial gradient spread method not supported | Very good |
| SVG2ContextFMX | All OS supported by Firemonkey: Windows, OsX, Android, iOS,.. | Implemented by Firemonkey | FMX | This is a rendercontext based on Delphi's FMX canvas implementations:
|
|
| SVG2ContextAgg | Windows, OsX | Aggpas | VCL, FMX | Good | Good |
| SVG2ContextGR32 | Windows, OsX | Graphics32 | VCL | Good | Good |
Render contexts for FPC Lazarus
| Render context | Supported OS* | Graphics library | Quality | Rendering speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVG2ContextD2D | Windows 7 and higher | Direct2D | Very good, some minor issues with the stroke-cap in combination with stroke-width. | Very good |
| SVG2ContextQuartz | OsX | Quartz | Good, radial gradient spread method not supported | Very good |
| SVG2ContextGR32 | Windows, Osx,Linux | Graphics32 | Good | Good |
| SVG2ContextAgg | Windows, OsX, Linux | Aggpas | Good | Good |
| SVG2BGRABitmap | Windows, Osx, Linux | BGRABitmap | Reasonable: some SVG features are not fully supported. | Good |
*Only the operating system on which the package is tested is shown.
Direct2D render context
Supprted operating systems:
Windows Vista, Win7, Win8, Win10
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, Delphi FMX (Wic only), FPC Lazarus
Library:
The required header files are included in the package, in folder Common\Platform.
Limitations:
Small issue with stroking in case of zero length path segments.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextD2D.pas
Remarks:
The Direct2D render context is the main render context for Windows. Quality and speed is very good. It has a great amount of functionality.
There are two types of Direct2D render contexts available, one is based on the "Windows Imaging Component" (WIC), this is available from Direct10 and upwards, the other is based in de "Direct11 Device context".
Some of the rendering with the Direct11 version will be hardware accelerated (if avaiable). This will be especially be noticable if you use filters, but on the other hand, copying buffers between GPU and CPU will be slow.
GDI+ render context
Supprted operating systems:
Windows XP, Vista, Win7, Win8, Win10
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, Delphi FMX
Library:
The required header files are included with Delphi
Limitations:
- Radial gradient only fills ellipses
- Radial gradient "spreadMethod" is not supported
- Radial gradient "focal point" is not supported
- Fill-rule not supported
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextGP.pas
Remarks:
The "Graphic Device Interface +" is mainly used as a fall back in cases DirectX is not available, for example on older XP versions.
Speed is good, quality is reasonable, the main problem is that svg-style radial gradients are not supported.
The GDI+ render context has the capability to render to EMS files.
Quartz render context
Supprted operating systems:
OsX and iOS
Supported platforms:
Delphi FMX, FPC Lazarus
Library:
The required header files are included with Delphi and FPC Lazarus
Limitations:
The radial gradient does not support the spread-method.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextQuartz.pas
Remarks:
Quarz is a graphics library for Apple's OsX and iOS.
Speed is good, Quality is overall good but the radial gradient does not support the spread-method.
The IOS support is tested with the IOS simulator only.
FMX canvas render context
Supprted operating systems:
All operating systems that Delphi Firemonkey supports for your particular Delphi version.
Supported platforms:
Delphi FMX
Library:
The required files are included with Delphi
Limitations:
- Can give different results on different platforms or different Delphi versions.
- Glyph rendering is not very precise on OsX, iOS and Android
- The butt stroke cap is not implemented, which results in some strokes being longer than intended
- Gradient implementation is lacking a lot of functionality
- On Android the GPU canvas is used, for filling shapes it relies on the device having a stencil buffer, but some devices dont use one.
- Delphi's stroke drawing algorithm for the GPU canvas, used for Android, doesn't give very good results
- Fill rule is not supported
The radial gradient does not support the spread-method.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextFMX.pas
Remarks:
The FMX render context is just a wrapper around Delphi's FMX canvas, On the positive side, this canvas supports a lot of operating systems, including Android (XE5 and higher). On the negative side, quality is not consistent. On Windows, FMX wil use Direct2D and quality will be reasonable but not as good as the dedicated Direct2D render context, because FMX doesn't use all available functionality of Direct2D. On Android for example overall quality of the rendered output is not very good. Also rendering text will not be as precise as with the dedicated render contexts.
Aggpas render context
Supprted operating systems:
Windows, OsX, Linux
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, Delphi FMX, FPC/Lazarus
Library
https://github.com/BVerhue/AggPasMod
Limitations:
Small issue with stroking in case of zero length path segments.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextAgg.pas
Remarks:
Aggpas is a port of the "Anti grain graphics library". Quality is good, speed is good.
Graphics32 render context
Supprted operating systems:
Windows (VCL, FPC) and Osx (FPC)
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, FPC/Lazarus
Library
https://github.com/graphics32/graphics32
Limitations:
Because SVG style gradients are not supported in this library, some code is borrowed from Aggpas to implement these using a custom polygon filler.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextGR32.pas
Remarks:
Graphics32 is a graphics library for Delphi and Lazarus. It is in principle a library for raster image processing, but it also has vector graphics capabilities implemented by the VPR vector graphics engine, the status of this extension is not really clear. Quality is good, speed is good.
BGRABitmap render context
Supprted operating systems:
Windows, Osx, Linux
Supported platforms:
FPC Lazarus
Library
https://github.com/bgrabitmap/bgrabitmap
Limitations:
- Gradient "spreadMethod" is not supported.
- Dash offset is not supported.
- Stroke thickness is not coupled to the Canvas2D transformation matrix. The approximation that is implemented here will give incorrect results in case of non-uniform scaling.
Unit:
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextBGRA.pas
Remarks:
BGRABitmap is a graphics library for FPC Lazarus. Quality is good, speed is good but it has some limitations for rendering SVG graphics.
Text layouts
For rendering of the <text> element, the library needs a font. At the moment the library supports two sources of fonts: "SVG fonts" or system fonts that are present on the local system.
SVG fonts
Officially "SVG fonts" are no longer supported by the SVG standard 2.0, but the SVG library still supports SVG fonts, because the advantage is that fonts can be used independent of the operating system. You can embed an SVG font directly into an SVG graphic or let your SVG graphic reference an external SVG font located in a seperate file. Examples of how to do this can be found in the "SVG 1.1 test suite".
There are multiple tools on the web to convert a TTF font to an SVG font.
The official way to go for fonts in SVG is with WOFF font files, but the library doesn't support this format at the moment. Of course using web fonts requires the device to be on-line when rendering the SVG containing the font.
System fonts
To access system fonts, the tools provided by the operating system can be used, for Windows this is GDI or DirectWrite and for OsX and iOS this is CoreText. In all other cases Freetype is used. If a particular font cannot be found, the system will use a fall back font, so It cannot be guaranteed that text will be rendered exactly the same on every device.
If you want your text to render exactly the same on each device the best way is to converting text elements to path elements. You can do this for example with "Inkscape".
The SVG control package uses a "ISVGFontSource" implementation as a library of fonts and a "ISVGTextLayout" implementation to format text.
The formatting of text consist of selecting fonts, applying fonts styles, bidi ordering of text, substitution of ligatures selecting glyphs, language specific processing and so on. This is done by the ISVGTextLayout implementation. After all that follows the SVG text processing for aligning, placing of individual glyphs or setting glyphs on a path.
Direct write
Supprted operating systems:
Windows Vista, Win7, Win8, Win10
Supported platforms:
Delphi FMX, FPC Lazarus
Library:
The required header files are included in the package, in folder Common\Platform
Limitations:
Have not found any.
Units
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2FontDirectWrite.pas
GDI fonts and Uniscribe
Supprted operating systems:
Windows XP, Vista, Win7, Win8, Win10
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, Delphi FMX
Library:
The required header files are included with Delphi, the header for Uniscribe is included in the package, in folder Common\Platform
Limitations:
Has sometimes trouble finding the correct font.
Units
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2FontGDI.pas
Core text
Supprted operating systems:
OsX and iOS
Supported platforms:
Delphi FMX, FPC Lazarus
Library:
The required header files are included with Delphi and FPC Lazarus
Limitations:
Have not found any.
Units
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2FontCoreText.pas
Freetype
Supprted operating systems:
See website
Supported platforms:
Delphi VCL, FMX, FPC Lazarus
Library:
The required header files are included in the package, in folder Common\Platform
Limitations:
- Has sometimes trouble finding the correct font.
- Does not contain a text formatter so the standard text formatter of the svg package is used, which does not support Arabic.
Units
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2FontFreetype.pas
FMX canvas text layout
Supprted operating systems:
All operating systems that Delphi Firemonkey supports for your particular Delphi version.
Supported platforms:
Delphi FMX
Library:
The required files are included with Delphi
Limitations:
- Glyph placement is not exact and quality can vary widely depending on the target OS.
- Does not contain a text formatter so the standard text formatter of the svg package is used, which does not support Arabic.
Units
Common\Platform\BVE.SVG2ContextFMX.pas
SVG types, interfaces and classes
Internally the library uses many different types, classes and interfaces. these mirror for a large part the definitions in the "SVG 1.1 specification".
For most applications, you do not need to know all the types, classes or interfaces, but just use text in SVG language, as described in the SVG 1.1 spec. to define the SVG graphic or create elements or set attribute values. The internal parser will convert the text into the appropriate type in the SVG hierarchy (DOM).
If you do need to find certain types, classes or interfaces, these can be found in the following units:
| Unit | Description |
|---|---|
BVE.SVG2Types.pas
|
Basic types and constants |
BVE.SVG2Intf.pas
|
Interface defininitions for SVG elements and render context objects |
BVE.SVG2Attributes.pas
|
SVG Attribute interface and implementation |
BVE.SVG2Elements.pas
|
Implementations for the SVG element interfaces |
BVE.SVG2Context.pas
|
implementations for the base render context and text layout objects |
BVE.SVG2PathData.pas
|
Pathdata class |
BVE.SVG2Bidi.pas
|
Contains an implementation of "UAX #9: Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm", used in case not provided by the text layout implementation |
BVE.BVE.SVG2CSSUtility.pas
|
CSS parsing and evaluation |
BVE.SVG2FilterUtility.pas
|
Implementation of filter effects, used in case not provided by the render context implementation |
BVE.SVG2GeomUtility.pas
|
Geometrical functions |
BVE.SVG2ParseUtility.pas
|
Base parser class and XML and SVG parser implementation |
BVE.SVG2SaxParser.pas
|
Builds the DOM tree using the XML reader |
BVE.SVG2XMLReader.pas
|
Parses XML files |
BVE.SVG2Doc.pas
|
TSVGDoc component |
Some interfaces and classes that are often needed when rendering SVG programmatically (see "Programming examples"):
| Class/interface | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TSVGSaxParser |
Common\BVE.SVG2SaxParser.pas
|
Class for parsing SVG text and converting it to a tree structure with SVG elements as nodes (DOM) represented by ISVGRoot |
| ISVGRoot |
Common\ISVGIntf.pas
|
Interface to the root of the DOM, this holds the SVG elements after parsing in a tree structure. |
| TSVGRootVCL |
Common\Vcl\BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL.pas
|
Implementation of the root for VCL. |
| TSVGRootFMX |
Common\Fmxl\BVE.SVG2Elements.FMX.pas
|
Implementation of the root for FMX. |
| TSVGRootFPC |
Common\Fpc\BVE.SVG2Elements.FPC.pas
|
Implementation of the root for FPC. |
| IXMLNode |
XML.XMLIntf(Delphi)
Common\BVE.SVG2Types.pas (FPC)
|
Interface for an XML node object, all SVG elements interfaces are derived from IXMLNode |
| ISVGElement |
Common\ISVGIntf.pas
|
Derived from IXMLNode, an interface to a SVG element. |
Some usefull procedures and functions
| Procedure/function | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SVGCreateElement |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Creates am SVG element |
| SVGCreateTextNode |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Creates a text node |
| SVGRenderToRenderContext |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Render a parsed SVG graphic represented by ISVGRoot to a ISVGRenderContext |
| SVGObjectAt |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Returns the element under the mousepointer of a parsed SVG graphic represented by ISVGRoot. [sroEvents] must be present in the RenderOptions property of ISVGRoot. |
| SVGMouseDown |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Passes an OnMouseDown event to ISVGRoot to process. If processed, this will trigger an OnSVGEvent on ISVGRoot. [sroEvents] must be present in the RenderOptions property of ISVGRoot. |
| SVGMouseMove |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Same for OnMouseMove |
| SVGMouseUp |
BVE.SVG2Elements
|
Same for OnMouseUp |
| SVGRenderToBitmap |
BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL
|
Render a parsed SVG graphic represented by ISVGRoot to a VCL bitmap. The render context used depends on the settings in Common\Vcl\ContextSettingsVCL.inc |
| SaveBitmapAsPng |
BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL
|
Save a VCL bitmap as Png |
| SaveBitmapAsJpg |
BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL
|
Save a VCL bitmap as Jpg |
| SVGRenderToBitmap |
BVE.SVG2Elements.FPC
|
Render a parsed SVG graphic represented by ISVGRoot to an FPC Lazarus bitmap. The render context used depends on the settings in Common\Vcl\ContextSettingsFPC.inc |
| SaveBitmapAsPng |
BVE.SVG2Elements.FPC
|
Save a VCL bitmap as Png |
| SaveBitmapAsJpg |
BVE.SVG2Elements.FPC
|
Save a VCL bitmap as Jpg |
| SVGRenderToBitmap |
BVE.SVG2Elements.FMX
|
Render a parsed SVG graphic represented by ISVGRoot to an FMX bitmap. The render context used depends on the settings in Common\Vcl\ContextSettingsFMX.inc |
Supported SVG features
The following table lists the supported SVG functionality for version 2.3 of the SVG package. The functionality marked with "Yes" is supported in basis but that doesn't always mean for 100%. If there is a known significant part of functionality missing, it is mentioned in the remark.
Limitations
- Quality of the output relies for a great deal on the underlying graphics library used for rasterizing, see section "Rendering contexts".
- There is no check on recursion on parsing an SVG document
- See remarks on following tables on further limitations
Elements
The following list indicates the implementation status of "svg elements" in the SVG library.
| SVG Element | Implemented | Type | Remarks |
| <a> | No | The a element is converted to a group element | |
| <altGlyph> | No |
|
|
| <altGlyphDef> | No |
|
|
| <altGlyphItem> | No |
|
|
| <animate> | No |
|
|
| <animateColor> | No |
|
|
| <animateMotion> | No |
|
|
| <animateTransform> | No |
|
|
| <circle> | Yes | ISVGCircle |
|
| <color-profile> | No |
|
|
| <cursor> | No |
|
|
| <clipPath> | Yes | ISVGClipPath |
|
| <defs> | Yes | ISVGDefs |
|
| <desc> | Yes | ISVGDesc |
|
| <ellipse> | Yes | ISVGEllipse |
|
| <feBlend> | Yes | ISVGFilterBlend |
|
| <feColorMatrix> | Yes | ISVGFilterColorMatrix |
|
| <feComponentTransfer> | Yes | ISVGFilterComponentTransfer |
|
| <feComposite> | Yes | ISVGFilterComposite |
|
| <feConvolveMatrix> | Yes | ISVGFilterConvolveMatrix |
|
| <feDiffuseLighting> | Yes | ISVGFilterDiffuseLighting |
|
| <feDisplacementMap> | Yes | ISVGFilterDisplacementMap |
|
| <feDistantLight> | Yes | ISVGFilterDistantLight |
|
| <feFlood> | Yes | ISVGFilterFlood |
|
| <feFuncA> | Yes | ISVGFilterFunc |
|
| <feFuncB> | Yes | ISVGFilterFunc |
|
| <feFuncG> | Yes | ISVGFilterFunc |
|
| <feFuncR> | Yes | ISVGFilterFunc |
|
| <feGaussianBlur> | Yes | ISVGFilterGuassianBlur |
|
| <feImage> | Yes | ISVGFilterImage |
|
| <feMerge> | Yes | ISVGFilterMerge |
|
| <feMergeNode> | Yes | ISVGFilterMergeNode |
|
| <feMorphology> | Yes | ISVGFilterMorphology |
|
| <feOffset> | Yes | ISVGFilterOffset |
|
| <fePointLight> | Yes | ISVGFilterPointLight |
|
| <feSpecularLighting> | Yes | ISVGFilterSpecularLighting |
|
| <feSpotLight> | Yes | ISVGFilterSpotlight |
|
| <feTile> | Yes | ISVGFilterTile |
|
| <feTurbulence> | Yes | ISVGFilterTurbulence |
|
| <filter> | Yes | ISVGFilter |
|
| <font> | Yes | ISVGFont |
|
| <font-face> | Yes | ISVGFontFace |
|
| <font-face-format> | Yes | ISVGFontFaceFormat |
|
| <font-face-name> | Yes | ISVGFontFaceName |
|
| <font-face-src> | Yes | ISVGFontFaceSrc |
|
| <font-face-uri> | Yes | ISVGFontFaceUri |
|
| <foreignObject> | No |
|
|
| <g> | Yes | ISVGGroup |
|
| <glyph> | Yes | ISVGGlyph |
|
| <glyphRef> | No |
|
|
| <hkern> | Yes | ISVGHKern |
|
| <image> | Yes | ISVGImage |
|
| <line> | Yes | ISVGLine |
|
| <linearGradient> | Yes | TSVGLinearGradient |
|
| <marker> | Yes | ISVGMarker |
|
| <mask> | Yes | ISVGMask |
|
| <metadata> | No |
|
|
| <missing-glyph> | No | ISVGGlyph is used | |
| <mpath> | No | ||
| <path> | Yes | ISVGPath |
|
| <pattern> | Yes | ISVGPattern |
|
| <polygon> | Yes | ISVGPolygon |
|
| <polyline> | Yes | ISVGPolyline |
|
| <radialGradient> | Yes | ISVGRadialGradient | Some render contexts do not fully support this, see "Render contexts". |
| <rect> | Yes | ISVGRect |
|
| <script> | No |
|
|
| <set> | No |
|
|
| <stop> | Yes | ISVGGradientPoint |
|
| <style> | Yes |
|
|
| <svg> | Yes | ISVG |
|
| <switch> | Yes | ISVGSwitch |
|
| <symbol> | Yes | ISVGSymbol |
|
| <text> | Yes | ISVGText |
|
| <textPath> | Yes | ISVGTextPath |
|
| <title> | Yes | ISVGTitle |
|
| <tref> | Yes | ISVGTextRef |
|
| <tspan> | Yes | ISVGSpan |
|
| <use> | Yes | ISVGUse |
|
| <view> | No |
|
|
| <vkern> | Yes | ISVGVKern |
|
Presentation attributes
This is a list indicates the implementation status of the "presentation attributes" in the SVG control library.
| Attribute | Implemented | Type | Remarks |
| alignment-baseline | No |
|
|
| baseline-shift | Yes | TSVGBaselineShift |
|
| clip-path | Yes | string |
|
| clip-rule | Yes | TSVGFillRule |
|
| clip | Yes | TSVGDimRect |
|
| color-interpolation-filters | Yes | TSVGColorSpace |
|
| color-interpolation | Yes | TSVGColorSpace |
|
| color-profile | No |
|
|
| color-rendering | No |
|
|
| color | Yes | TSVGColor |
|
| cursor | No |
|
|
| direction | Yes | TSVGDirection |
|
| display | Yes | TSVGDisplay |
|
| dominant-baseline | No |
|
|
| enable-background | No |
|
This attribute is to be removed from the SVG specs. and is replaced by the "isolation" attribute |
| fill-opacity | Yes | TSVGFloat |
|
| fill-rule | Yes | TSVGFillRule |
|
| fill | Yes | TSVGPaint |
|
| filter | Yes | string |
|
| flood-color | Yes | TSVGPaint |
|
| flood-opacity | Yes | TSVGFloat |
|
| font-family | Yes | TFontName |
|
| font-size-adjust | No |
|
|
| font-size | Yes | TSVGFontSize |
|
| font-stretch | Yes | TSVGFontStretch |
|
| font-style | Yes | TSVGFontStyle |
|
| font-variant | Yes | TSVGFontVariant |
|
| font-weight
|
Yes | TSVGFontWeight |
|
| glyph-orientation-horizontal
|
No
|
|
|
| glyph-orientation-vertical
|
No
|
|
|
| image-rendering
|
No
|
|
|
| isolation | Yes | TSVGIsolationMode |
|
| Kerning
|
No
|
|
|
| letter-spacing | Yes | TSVGSpacing |
|
| lighting-color | Yes | TSVGPaint |
|
| marker | Yes | string |
|
| marker-start | Yes | string |
|
| marker-mid | Yes | string |
|
| marker-end | Yes | string |
|
| mask | Yes
|
string
|
|
| opacity | Yes | TSVGFloat |
|
| overflow | Yes | TSVGOverflow |
|
| pointer-events | Yes | TSVGPointerEventsType |
|
| shape-rendering
|
No
|
|
|
| stop-color | Yes | TSVGPaint
|
|
| stop-opacity | Yes | TSVGFloat
|
|
| stroke | Yes | TSVGPaint |
|
| stroke-opacity | Yes | TSVGFloat |
|
| stroke-width | Yes | TSVGDimension |
|
| stroke-linecap | Yes | TSVGStrokeCap |
|
| stroke-linejoin | Yes | TSVGStrokeJoin |
|
| stroke-miterlimit | Yes | TSVGFloat
|
|
| stroke-dasharray | Yes | TSVGDimArray |
|
| stroke-dashoffset | Yes | TSVGDimension |
|
| text-anchor | Yes | TSVGTextAnchor |
|
| text-decoration | Yes
|
TSVGTextDecoration
|
|
| text-rendering | No |
|
|
| unicode-bidi | Yes | TSVGUnicodeBidi
|
|
| visibility | Yes | TSVGVisibility |
|
| word-spacing
|
No
|
|
|
| writing-mode | Yes | TSVGWritingMode |
|
CSS
CSS is implemented as case-sensitive at the moment. Anything that is not on the list is not supported.| Selector types | Implemented |
| * (All) | Yes |
| <element> | Yes |
| Selectors |
|
| . (Class) | Yes |
| # (ID) | Yes |
| Attribute | Yes |
| PseudoClass | Yes |
| PseudoClassTypes |
|
| FirstChild | Yes |
| LastChild (not possible with the sax-parser)
|
No |
| NthChild | Yes |
| Language | Yes |
| others... | No |
| Attribute evaluators |
|
| Name only | Yes |
| = (Equal) | Yes |
| ~= (Contains word) | Yes |
| |= (Begins with word) | Yes |
| ^= (Begins with part of word) | Yes |
| $= (Ends with word) | Yes |
| *= (Contains part of word) | Yes |
| others... | No |
| Combinators |
|
| (Descendant) | Yes |
| > (Direct descendant) | Yes |
| + (Adjacent) | Yes |
| ~ (Preceding) | Yes |
| others... | No |
| Properties |
|
| See list of attributes |
|
Programming examples
Here are some examples on how to use the package for rendering and modifying SVG graphics programmatically.
- Assign an SVG to a TSVG2Image
- Create a simple digital clock
- Create a filter graph
- Assign an SVG to a TSVG2Graphic object and assign to a standard TImage
- Render SVG programmatically
- Find and element the easy way
- Find and element the hard way: traverse the DOM tree
- Change an attribute
- Setting style attributes
- Add and remove elements
- Add an SVG fragment
- Find element under the mouse pointer
- Using mouse events
- Loading files from internet
The source code for these examples can be found in Examples\ExamplesFromDoc.
Assign an SVG to a TSVG2Image
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
In the "OnCreate" event handler of the form put the following (replace.. with a valid path to the img folder)
Code
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.Filename := '..\Img\Butterfly.svg';
end;
Create a simple digital clock
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
For Delphi VCL set the "DoubleBuffered" property of the form to "True", to surpress flicker.
Put a TTimer on the form.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
const
svg_clock =
'<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1"'
+ ' viewBox="0 0 200 80">'
+ '<g font-family="courier new" font-size="24" text-anchor="middle">'
+ '<text x="100" y="30" fill="blue" >%s</text>'
+ '<text x="100" y="60" fill="blue" >%s</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '<rect x="1" y="1" width="198" height="78" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := Format(svg_clock, [DateToStr(Now), TimeToStr(Now)]);
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
Create a filter graph
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
For Delphi VCL set the "DoubleBuffered" property of the form to "True", to surpress flicker.
Create an "OnCreate" handler on the form.
Add the following code to the unit.
Code
uses
BVE.SVG2Types;
const
// Filter borowed from here: http://luxor-xul.sourceforge.net/talk/jug-nov-2002/slides.html
svg_filter = '<filter id="%s" width="%s" height="%s">%s</filter>';
svg_filter_gaussian =
'<feGaussianBlur in="%s" result="%s" stdDeviation="%d" />';
svg_filter_offset =
'<feOffset in="%s" result="%s" dx="%d" dy="%d" />';
svg_filter_composite =
'<feComposite in="%s" in2="%s" result="%s" operator="%s" />';
svg_filter_spec_light =
'<feSpecularLighting in="%s" result="%s"'
+ ' surfaceScale="%d" specularConstant="%d" specularExponent="%d"'
+ ' kernelUnitLength="1" lighting-color = "%s">%s</feSpecularLighting>';
svg_filter_light_distant =
'<feDistantLight azimuth="%d" elevation="%d" />';
svg_filter_text =
'<svg>'
+ '%s'
+ '<g font-size="100" font-weight="bold">'
+ '<text x="20" y="320" fill="%s" filter="url(#myFilter)">%s</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var
Filter: string;
begin
SVG2Image1.RenderOptions := [sroFilters, sroClippath];
Filter :=
Format(svg_filter, ['myFilter', '120%', '150%',
Format(svg_filter_gaussian, ['SourceAlpha', 'gauss1', 6])
+ Format(svg_filter_offset, ['gauss1', 'offset', 5, 5])
+ Format(svg_filter_composite, ['SourceGraphic', 'offset', 'comp1', 'over'])
+ Format(svg_filter_gaussian, ['SourceAlpha', 'gauss2', 2])
+ Format(svg_filter_spec_light, ['gauss2', 'spec', -3, 1, 16, 'white',
Format(svg_filter_light_distant, [45, 45])
])
+ Format(svg_filter_composite, ['spec', 'SourceGraphic', 'comp2', 'in'])
+ Format(svg_filter_composite, ['comp2', 'comp1', 'comp3', 'over'])
]);
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := Format(svg_filter_text, [filter, 'red', 'SVG rocks!']);
end;
Assign an SVG to a TSVG2Graphic object and assign to a standard TImage
The TSVG2Graphic class is derived from TGraphic, so you can use it in a standard (Delphi or FPC) TImage object.
Put a TImage object on a form.
Set the "Align" property of the Image1 object to "alClient".
Set the "Stretch" property of the Image1 object to "True"
Put the following code in the "OnCreate" handler of the form (replace .. with a valid path to the img folder):
Code
uses
{$IFnDEF FPC}
BVE.SVG2Graphic.VCL;
{$ELSE}
BVE.SVG2Graphic.FPC;
{$ENDIF}
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var
Graphic: TSVG2Graphic;
begin
Graphic := TSVG2Graphic.Create;
try
Graphic.LoadFromFile('..\Img\Butterfly.svg');
Image1.Picture.Assign(Graphic);
finally
Graphic.Free;
end;
end;
Render SVG programmatically
Here is an example how to load an SVG graphic from file, parse it and render it to a bitmap.
For FPC Lazarus, there is a small difference, we render to an interface to a bitmap in stead of to a bitmap directly. This has to do with differences in widget set implementations.
Put a TButton on a form and put a TOpenFIle dialog object on the form.
On the Button1 "OnClick" event handler put the following.
Add the following code to the unit.
Code
uses
{$IFnDEF FPC}
BVE.SVG2Elements.VCL,
{$ELSE}
BVE.SVG2Elements.FPC,
{$ENDIF}
BVE.SVG2Intf,
BVE.SVG2SaxParser;
procedure TfrmRenderProgrammatically.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
{$IFnDEF FPC}
var
FileName: string;
SVGParser: TSVGSaxParser;
SVGRoot: ISVGRoot;
Bitmap: TBitmap;
begin
// Code for Delphi VCL
if OpenDialog1.Execute then
begin
FileName := OpenDialog1.FileName;
// Create a root to store the SVG rendering tree
SVGRoot := TSVGRootVcl.Create;
// Create a SAX parser instance
SVGParser := TSVGSaxParser.Create(nil);
try
// Parse SVG document and build the rendering tree
SVGParser.Parse(FileName, SVGRoot);
// Create a bitmap
Bitmap := TBitmap.Create;
try
Bitmap.PixelFormat := TPixelFormat.pf32bit; // 32bit bitmap
Bitmap.AlphaFormat := TAlphaFormat.afDefined; // Enable alpha channel
Bitmap.SetSize(480, 320); // Set desired size
Bitmap.Canvas.Brush.Color := clNone; // Fill background with transparent
Bitmap.Canvas.FillRect(Rect(0, 0, 480, 320));
// Render the SVG onto the bitmap
SVGRenderToBitmap(
SVGRoot, // The root containing the rendering tree
Bitmap // The destination bitmap
);
// Do something with the bitmap...
Canvas.Draw(30, 30, Bitmap);
finally
Bitmap.Free;
end;
finally
SVGParser.Free;
end;
end;
end;
{$ELSE}
var
FileName: string;
SVGParser: TSVGSaxParser;
SVGRoot: ISVGRoot;
IntfBitmap: ISVGIntfBitmap;
Bitmap: TBitmap;
begin
// Code for FPC Lazarus
if OpenDialog1.Execute then
begin
FileName := OpenDialog1.FileName;
// Create a root to store the SVG rendering tree
SVGRoot := TSVGRootFpc.Create;
// Create a SAX parser instance
SVGParser := TSVGSaxParser.Create(nil);
try
// Parse SVG document and build the rendering tree
SVGParser.Parse(FileName, SVGRoot);
// Create an interface bitmap.
// Because of differences in widget set implementations we cannot
// render to a bitmap directly, but must use an interface with the
// appropriate implementation.
IntfBitmap := SVGCreateIntfBitmap(480, 320);
// Render the SVG onto the interface bitmap
SVGRenderToBitmap(
SVGRoot, // The root containing the rendering tree
IntfBitmap // The destination bitmap
);
// Create a bitmap from the interface bitmap
Bitmap := IntfBitmap.CreateBitmap;
try
// Do something with the bitmap...
Canvas.Draw(30, 30, Bitmap);
finally
Bitmap.Free;
end;
finally
SVGParser.Free;
end;
end;
end;
{$ENDIF}
Find and element the easy way
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
For Delphi VCL set the "DoubleBuffered" property of the form to "True", to surpress flicker.
Create an "OnCreate" and an "OnKeyDown" handler on the form.
Add the following code to the unit.
Code
uses
BVE.SVG2Intf;
const
svg_text =
'<svg viewBox="0 0 200 80">'
+ '<g font-family="courier new" text-anchor="middle">'
+ '<text id="text1" x="100" y="30" font-size="16" fill="blue" ></text>'
+ '<text id="text2" x="100" y="60" font-size="24" fill="red" ></text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '<rect x="1" y="1" width="198" height="78" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_text;
end;
procedure TForm1.FormKeyDown(Sender: TObject; var Key: Word;
Shift: TShiftState);
var
Element: ISVGElement;
ShiftValue: string;
begin
// Find element with id = 'text1'
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['text1'];
if assigned(Element) then
begin
ShiftValue := '';
if ssShift in Shift then
ShiftValue := ShiftValue + '[Shift]';
if ssAlt in Shift then
ShiftValue := ShiftValue + '[Alt]';
if ssCtrl in Shift then
ShiftValue := ShiftValue + '[Ctrl]';
Element.Text := ShiftValue;
end;
// Find element with id = 'text2'
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['text2'];
if assigned(Element) then
begin
Element.Text := IntToStr(Key);
end;
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
Find and element the hard way: traverse the DOM tree
Sometimes you need to evaluate all nodes in an SVG graphic.
The following code traverses the DOM tree and outputs the structure to a memo.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
Put a TMemo on the form.
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnAfterParse" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
uses
...
{$IFnDEF FPC}
XML.XMLIntf;
{$ELSE}
BVE.SVG2Types;
{$ENDIF}
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
SVG2Image1: TSVG2Image;
Memo1: TMemo;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure SVG2Image1AfterParse(Sender: TObject);
private
procedure DoNode(aLevel: integer; aNode: IXMLNode);
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses
BVE.SVG2Intf;
const
svg_text =
'<svg viewBox="0 0 200 80">'
+ '<g font-family="courier new" text-anchor="middle">'
+ '<text id="text1" x="100" y="30" font-size="16" fill="blue" >Blue</text>'
+ '<text id="text2" x="100" y="60" font-size="24" fill="red" >Red</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '<rect x="1" y="1" width="198" height="78" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '</svg>';
type
TOnNodeEvent = procedure(aLevel: integer; aNode: IXMLNode) of object;
procedure Traverse(aNode: IXMLNode; aLevel: integer; aProcNode: TOnNodeEvent);
var
i: integer;
begin
aProcNode(aLevel, aNode);
for i := 0 to aNode.ChildNodes.Count - 1 do
Traverse(aNode.ChildNodes[i], aLevel + 1, aProcNode);
end;
procedure TForm1.DoNode(aLevel: integer; aNode: IXMLNode);
var
Info: string;
begin
Info := '<' + aNode.LocalName + '>';
if aNode.HasAttribute('id') then
Info := Info + ' id: ' + aNode.Attributes['id'];
Memo1.Lines.Add(StringOfChar(' ', aLevel*4) + Info);
end;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_text;
end;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1AfterParse(Sender: TObject);
begin
Memo1.Clear;
{$IFnDEF FPC}
Traverse(SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG, 0, DoNode);
{$ELSE}
Traverse(SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG, 0, @DoNode);
{$ENDIF}
end;
Change an attribute
The following example changes the "transform" attribute of a group element.
For Delphi VCL set the "DoubleBuffered" property of the form to "True", to surpress flicker.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
Put a TTimer on the form.
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnAfterParse" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add an "OnTimer" event handler on the Timer1 object.
Set the folowing properties of Timer1:
"Enabled = False"
"Interval = 25"
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
SVG2Image1: TSVG2Image;
Timer1: TTimer;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure SVG2Image1AfterParse(Sender: TObject);
procedure Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
private
t: integer;
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses
BVE.SVG2Intf;
const
svg_transform =
'translate(%3.2f,%3.2f) rotate(%3.2f)';
svg_orbit =
'<svg width="200" height="200" viewBox="0 0 200 200">'
+ '<ellipse cx="100" cy="100" rx="100" ry="100" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '<g id="g1">'
+ '<circle cx="0" cy="0" r="20" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '<text x="0" y="12" text-anchor="middle" font-size="36" fill="blue" >A</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_orbit;
end;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1AfterParse(Sender: TObject);
begin
t := 0;
Timer1.Enabled := True;
end;
procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
var
Element: ISVGElement;
A1, A2, Ar: Double;
begin
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['g1'];
if assigned(Element) then
begin
A1 := 360*(t mod 100)/100;
Ar := A1*PI/180;
A2 := -A1*100/20;
Element.Attributes['transform'] :=
Format(svg_transform, [100+80*Cos(Ar), 100+80*Sin(Ar), A2]);
end;
Inc(t);
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
Setting style attributes
In SVG there are three ways to define style:
- With an element attribute, for example:
<rect width="50" height="50" fill="red"/> - With a css style sheet, for example:
<style type="text/css">
rect {fill: red; stroke: none;}
</style>
<rect width="50" height="50" /> - With an inline css style attribute, for example:
<rect width="50" height="50" style="fill: red; stroke: none;"/>
The priority in which style is evaluated is 3, then 2, then 1, so inline style overrules style sheet style which in turn overrules the attribute style.
The following example demonstrates setting style.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnClick" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
uses
BVE.SVG2Intf;
const
svg_style1 =
' text {'
+ ' font-family: "courier new";'
+ ' font-size: 24;'
+ ' }';
svg_style2 =
' text {'
+ ' font-family: "arial";'
+ ' font-size: 16;'
+ ' }';
svg_text =
'<svg viewBox="0 0 200 80">'
+ '<style id="stylesheet" type="text/css">'
+ svg_style1
+ '</style>'
+ '<g text-anchor="middle">'
+ '<text id="text1" x="100" y="30" fill="blue" >Blue</text>'
+ '<text id="text2" x="100" y="60" fill="red" >Red</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '<rect x="1" y="1" width="198" height="78" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_text;
end;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
Element: ISVGElement;
begin
// Change inline style (highes priority)
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['text2'];
if assigned(Element) then
Element.Attributes['style'] := 'font-family: "Times New Roman"; font-size: 24';
// Change style sheet (medium priority)
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['stylesheet'];
if assigned(Element) then
Element.Text := svg_style2;
// Change attribute (lowest priority, this will have no effect)
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['text1'];
if assigned(Element) then
Element.Attributes['font-family'] := 'Georgia';
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
Add and remove elements
The following example shows how to add or remove elements.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form and set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnClick" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
SVG2Image1: TSVG2Image;
procedure SVG2Image1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
private
FStep: integer;
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses
{$IFnDEF FPC}
XML.XMLIntf,
{$ENDIF}
BVE.SVG2Types,
BVE.SVG2Elements,
BVE.SVG2Intf;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
FStep := 0;
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := '';
end;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
Node: IXMLNode;
begin
case FSTep of
0: begin
Node := SVGCreateElement(TSVGIri.Empty, el_svg);
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVGList.Add(Node);
Node.Attributes['width'] := '10cm';
Node.Attributes['height'] := '8cm';
Node.Attributes['viewBox'] := '0 0 100 80';
Caption := 'SVG element created';
Inc(FStep);
end;
1: begin
Node := SVGCreateElement(TSVGIri.Empty, el_rect);
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG.ChildNodes.Add(Node);
Node.Attributes['id'] := 'rect';
Node.Attributes['x'] := 0;
Node.Attributes['y'] := 0;
Node.Attributes['width'] := 100;
Node.Attributes['height'] := 80;
Node.Attributes['style'] := 'fill: yellow; stroke: blue;';
Caption := 'Rect element created';
Inc(FStep);
end;
2: begin
Node := SVGCreateElement(TSVGIri.Empty, el_ellipse);
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG.ChildNodes.Add(Node);
Node.Attributes['cx'] := 50;
Node.Attributes['cy'] := 40;
Node.Attributes['rx'] := 50;
Node.Attributes['ry'] := 40;
Node.Attributes['style'] := 'fill: none; stroke: red;';
Caption := 'Ellipse element created';
Inc(FStep);
end;
3: begin
Node := SVGCreateElement(TSVGIri.Empty, el_text);
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG.ChildNodes.Add(Node);
Node.Attributes['x'] := 50;
Node.Attributes['y'] := 45;
Node.Attributes['text-anchor'] := 'middle';
Node.Attributes['style'] := 'font-family: "times"; font-size: 24; fill: red;';
Node.Text := 'Ready...';
Caption := 'Text element created';
Inc(FStep);
end;
4: begin
Node := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['rect'];
if assigned(Node) then
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG.ChildNodes.Remove(Node);
Caption := 'Rect element removed';
Inc(FStep);
end;
5: begin
SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.SVG.ChildNodes.Clear;
Caption := 'SVG child list cleared';
FStep := 1;
end;
end;
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
Add an SVG fragment
Apart from adding elements one by one your can also add multiple elements at once to the ChildList of a node.
Method "AddFragment" of ISVGElement allows you to parse an xml fragment and add the result to the Childlist of the element.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
Add an "OnClick" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
uses
BVE.SVG2Intf;
const
svg_text =
'<svg viewBox="0 0 200 80">'
+ '<g text-anchor="middle">'
+ '<rect x="20" y="20" width="160" height="40" fill="#101010" stroke="#CCCCCC" stroke-width="2" />'
+ '<text id="text" x="100" y="45" fill="white" >Click me...</text>'
+ '</g>'
+ '<rect x="1" y="1" width="198" height="78" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="1" />'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_text;
end;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
Element: ISVGElement;
begin
Element := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.Element['text'];
if assigned(Element) then
begin
Element.ChildNodes.Clear;
Element.AddFragment('<tspan fill="yellow">Button <tspan fill="red" font-weight="bold" text-decoration="underline">clicked!</tspan></tspan>');
SVG2Image1.Repaint;
end;
end;
Find element under the mousepointer
The following example shows how to get an element that is under the mousepointer.Only elements with physical dimensions can receive mousepointer events, these are elements that support the ISVGObject interface.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
Set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
Set the "Filename" property of SVG2Image1 to "animated-clock.svg" in the "Img" folder.
Set property "RenderOptions" to include "sroEvents" (for example [sroClippath,sroEvents]), this will enable catching mousepointer events.
Add an "OnMouseDown" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit. The clicked element will be shown in the form's caption.
uses
BVE.SVG2Types,
BVE.SVG2Intf;
procedure TForm1.SVG2Image1MouseDown(Sender: TObject; Button: TMouseButton;
Shift: TShiftState; X, Y: Integer);
var
SVGObject: ISVGObject;
begin
SVGObject := SVG2Image1.SVGRoot.ObjectAtPt(SVGPoint(X, Y), FALSE);
if assigned(SVGObject) then
Caption := SVGObject.LocalName + ' id:' + SVGObject.ID
else
Caption := 'No object';
end;
Using mouse events
The following example shows how to use SVGpointer events.
The mouse event that you want to catch must be defined in the SVG graphic.
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
Set property "Align" of the SVG2Image1 to "alClient".
Set property "RenderOoptions" to "[sroClippath,sroEvents]"
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form,.
Add an "OnSVGEvent" event handler to the SVG2Image1 object.
Add the following code to the unit.
All info linked to the event will be accessible through the ISVGEvent interface, which is passed to the event handler.
Code
uses
...
BVE.SVG2Intf;
type
TfrmMouseEvents = class(TForm)
SVG2Image1: TSVG2Image;
procedure SVG2Image1SVGEvent(Sender: TObject; aSVGRoot: ISVGRoot;
aEvent: ISVGEvent; const aValue: string);
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
frmMouseEvents: TfrmMouseEvents;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses
BVE.SVG2Types;
const
svg_events =
'<svg width="6cm" height="5cm" viewBox="0 0 600 500"'
+ ' xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1"'
+ ' xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">'
+ '<defs>'
+ '<ellipse id="ellipse_large" cx="300" cy="250" rx="300" ry="200" />'
+ '</defs>'
+ '<use id="use_back" onmouseover="MouseOver!" onmouseout="MouseOut!" onmousemove="MouseMove!" fill="red" stroke="black" stroke-width="1" xlink:href="#ellipse_large" />'
+ '<use id="use_left" onmouseover="MouseOver!" onmouseout="MouseOut!" onmousemove="MouseMove!" fill="green" stroke="black" stroke-width="4" transform="translate(-50,250) scale(0.25)" xlink:href="#ellipse_large" />'
+ '<use id="use_right" onmouseover="MouseOver!" onmouseout="MouseOut!" onmousemove="MouseMove!" fill="blue" stroke="black" stroke-width="4" transform="translate(500,250) scale(0.25)" xlink:href="#ellipse_large" />'
+ '</svg>';
procedure TfrmMouseEvents.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
SVG2Image1.SVG.Text := svg_events;
end;
procedure TfrmMouseEvents.SVG2Image1SVGEvent(Sender: TObject;
aSVGRoot: ISVGRoot; aEvent: ISVGEvent; const aValue: string);
var
Info: string;
begin
if aEvent.EventType <> etNone then
begin
// Only the eventtypes defined in the SVG will be catched!
Info := aEvent.CurrentTarget.LocalName + ' id: ' + aEvent.CurrentTarget.ID + ' event: ';
case aEvent.EventType of
etClick:
Info := Info + 'click';
etMouseDown:
Info := Info + 'mouseDown';
etMouseUp:
Info := Info + 'mouseUp';
etMouseOut:
Info := Info + 'mouseOut';
etMouseMove:
Info := Info + 'mouseMove';
etMouseOver:
Info := Info + 'mouseOver';
end;
end else
Info := '';
Caption := Info;
end;
Loading files from internet
The following example shows how to load files from internet.
Requirements for downloading files directly from the internet:
- Define InternetAccess must be enabled in CompilerSettings.inc.
- For SSL (https) libeay32.dll and ssleay32.dll must be available on the system. Download from https://indy.fulgan.com/SSL/
The example loads SVG files from the SVG1.1 test suite and loads the corresponding Png file and then displays them side by side.
To enable loading files from internet the define "SVGInternetAccess" must be enabled in include file "Common\CompilerSettings.inc".
Put a TSVG2Image on a form.
Next to it, put a TImage control on the form.
Set width = 480 and height = 360 on both controls.
Put a TButton on the form.
Add an "OnCreate" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnDestroy" event handler to the form.
Add an "OnClick" event handler to the Button1 object.
Add the following code to the unit:
Code
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
SVG2Image1: TSVG2Image;
Image1: TImage;
Button1: TButton;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure FormDestroy(Sender: TObject);
procedure Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
private
FStep: integer;
Fsl: TStringList;
FPath: string;
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses
BVE.SVG2SaxParser,
BVE.SVG2Types,
PngImage;
procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
p: integer;
Filename: string;
MemStream: TMemoryStream;
Png: TPngImage;
begin
if FStep >= Fsl.Count then
FStep := 0;
if FStep < Fsl.Count then
begin
FileName := Fsl[FStep];
Caption := FileName;
try
// Load the SVG file
SVG2Image1.FileName := FPath + 'svg/' + FileName;
// Load the corresponding Png file
MemStream := TMemoryStream.Create;
try
p := Pos('.', FileName);
Png := TPngImage.Create;
try
TSVGSaxParser.LoadFromInternet(FPath + 'png/' + copy(FileName, 1, p - 1) + '.png', MemStream);
MemStream.Position := 0;
Png.LoadFromStream(MemStream);
Image1.Picture.Graphic := Png;
finally
Png.Free;
end;
finally
MemStream.Free;
end;
except on E:Exception do
begin
Caption := Caption + ' Error: ' + E.Message;
end;
end;
end;
FStep := FStep + 1;
end;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var
MemStream: TMemoryStream;
i: integer;
begin
SVG2Image1.RenderOptions := [sroClippath, sroFilters];
FPath := 'https://dev.w3.org/SVG/profiles/1.1F2/test/';
Fsl := TStringList.Create;
MemStream := TMemoryStream.Create;
try
// Load the list of files in the SVG1.1 test suite
TSVGSaxParser.LoadFromInternet(FPath + '/svg/basic-files.txt', MemStream);
TSVGSaxParser.LoadFromInternet(FPath + '/svg/tiny-files.txt', MemStream);
TSVGSaxParser.LoadFromInternet(FPath + '/svg/full-files.txt', MemStream);
MemStream.Position := 0;
Fsl.LoadFromStream(MemStream);
// Delete the testfiles that are not supprted
i := 0;
while i < Fsl.Count do
begin
// Note: not all test svg's will render correctly, filter out the
// svg groups that are not supported in any case.
if (Pos('animate-', Fsl[i])<>0)
or (Pos('interact-', Fsl[i])<>0)
or (Pos('script-', Fsl[i])<>0)
or (Pos('struct-dom-', Fsl[i])<>0)
or (Pos('text-dom-', Fsl[i])<>0)
or (Pos('text-tselect-', Fsl[i])<>0)
then
Fsl.Delete(i)
else
Inc(i);
end;
Fsl.Sort;
finally
MemStream.Free;
end;
FStep := 0;
Button1Click(Self);
end;
procedure TForm1.FormDestroy(Sender: TObject);
begin
Fsl.Free;
end;
SVG Viewer applications
The purpose of these viewer applications is to demonstrate the functionality of the SVG package but also to provide some coding examples for working with the SVG in application development.
SVG viewer VCL
The demo viewer is a viewer for SVG graphics and build with the VCL framework, so Windows only.
- You can load SVG graphics from file, or you can drag them into the application from the file explorer.
- You can create a new empty SVG or edit the SVG content and then parse it.
- You can also copy and paste SVG graphics as text, or make a "direct copy", this will copy the rendering tree.
- You can enable or disable the "AutoViewbox" property.
- You can enable or disable SVG filters.
- You can also drag and drop SVG files into the application.
- You can export a SVG graphic or a group of SVG graphics as png, jpeg or bitmap file.
- The "About" form displays an SVG graphic that has some SVG event functionality defined.
- Loading the "Animated clock" will show some animation and interaction: it will show the current time and you can manipulate the clock hands by mouse.
- The application is DPI aware
SVG viewer FMX
The demo viewer is a viewer for SVG graphics and build with the FMX framework, it compiles on all platforms.
It has more or less the same functionality as the VCL viewer, but additionally it also supports global scalling, with the slider on the right.
Bug reporting
It is not unlikely that at some point you run into a bug. I spend a lot of time testing, but considering that the package supports 10 Delphi versions, the VCL, FMX and FPC Lazarus platform and possibly 4 operating systems, the number of test scenarios add up and some bugs may slip through.
If you find a bug you can send me an email at BVerhue@gmail.com and I will do my best to solve it.
In your bug report please name:
- the Delphi or FPC and Lazarus version you are using
- the platform you are using (VCL or FMX or FPC Lazarus)
- the operating system
- and if possible send the SVG graphic that triggers the bug.
It is not guaranteed that I can solve everything, some render contexts are limited or do not support all functionality needed for rendering the full SVG specification. See sections "Render contexts" and "Text layouts" for known limitations.
Future development
With this new version I hope I made another step to a more complete and more useful SVG implementation for Delphi and FPC Lazarus. Of course adding SVG functionality is something I will keep on doing.
If you have any suggestions for the control, you can send it to me. I can't guaranty I will be able to implemented it, but I'll have a go. I am developing this control in my free time so I don't have an unlimited time for development.
See the website for updates and more examples
https://www.bverhue.nl/delphisvgBruno Verhue, Delft 2019
BVerhue@gmail.com
License
See the order page on the Delphi SVG site or see the License.txt that is included in the package.